Discover expert tips and detailed guides on metal riveting techniques tools and applications for DIY and professional fabricators.
If you’re working with metal, knowing how to master metal riveting can be a game changer. Whether you’re a DIYer tackling home repairs or a professional fabricator building something strong and lasting, metal riveting offers a reliable, vibration-resistant way to join metal parts without the complications of welding. In this guide, you’ll discover the essential techniques, tools, and best practices for creating durable joints that stand the test of time. Ready to unlock the secrets behind this timeless fastening method? Let’s dive in!
The History and Evolution of Metal Riveting
Metal riveting has been a trusted method for joining materials for thousands of years. Its roots trace back as far as 4,000 BCE in ancient Egypt, where craftsmen used rivets in tools and weapons during the Bronze Age. This early adoption highlights how reliable and strong riveting has always been, standing the test of time through centuries.
The technique took a major leap during the Industrial Revolution. In the 19th century, riveting became essential for constructing boilers and bridges, where sturdy, permanent joints were a must. World War I introduced innovations like blind rivets, which allowed installation from one side—a game changer for wartime repairs and complex assemblies.
Today, metal riveting continues evolving with modern industries like aerospace and automotive manufacturing pushing the boundaries. Eco-friendly cold riveting methods reduce heat use and energy consumption, making the process more sustainable. Brands like Vast have developed beginner-friendly rivet kits that bring professional-quality tools and materials right to DIY enthusiasts and professionals alike, allowing easier access to this timeless metal joining technique.
Have you ever wondered how ancient methods shaped today’s metal riveting tools? What modern trends excite you the most?
Types of Rivets Selecting the Right One for Your Metal Project

When it comes to metal riveting, choosing the right type of rivet is key to a strong, lasting joint. Here’s a quick breakdown of the most common rivet types and what they’re best for.
Solid Rivets
These are the go-to for heavy-duty jobs. Solid rivets offer high strength and are often used in structural work like bridges and aircraft. They require access to both sides of the material for installation, which can be a downside for some projects. Pros include excellent shear strength and durability, but they take more time and skill to install.
Blind Pop Rivets
Blind rivets are great when you can only reach one side of the material. Popular in automotive and home repairs, pop rivets provide good corrosion resistance and are quick to install. They work well for sheet metal and are often aluminum or stainless steel. Keep in mind their strength isn’t as high as solid rivets, so they’re not the best choice for structural applications.
Tubular and Semi-Tubular Rivets
These lightweight rivets are common in electronics and HVAC work. Their hollow design makes installation easier and consumes less material, reducing weight. They usually provide moderate strength, perfect for joining thinner metals where full structural strength isn’t needed.
Other Specialized Rivets
You’ll find split drive and flush rivets used in niche cases. Split drive rivets expand upon installation, offering solid retention in softer materials, while flush rivets sit flush with the surface for a smooth finish—ideal for aerospace skins. The material you choose matters too; aluminum rivets resist corrosion well, while steel rivets handle higher stress.
How to Choose
When picking a rivet, consider these factors:
- Grip Range: Make sure the rivet length matches the thickness of your materials.
- Shear Strength: Choose based on the load your joint will face.
- Cost: Blind rivets are usually more affordable and faster to use, but solid rivets last longer under stress.
For most projects, balancing strength and ease of installation helps you decide the best rivet type.
Selecting the right rivet upfront saves time and gives you a reliable hold every time.
Essential Tools and Materials for Effective Metal Riveting
To get metal riveting right, having the right tools and materials is key—whether you’re a DIYer or working on a bigger project.
Hand Tools for DIY Riveting
- Hammers: A good riveting hammer is lightweight with a flat face to shape the rivet head without damaging the metal.
- Bucking Bars: These metal bars provide a solid backing when compressing solid rivets, helping form a strong joint.
- Drill Bits: Use sharp bits sized just right for your rivet diameter to make clean, precise holes.
Power Tools Pneumatic vs Hydraulic Rivet Guns
- Pneumatic Rivet Guns: Most popular for their speed and ease, these tools use compressed air and are perfect for medium-heavy jobs.
- Hydraulic Rivet Guns: Offer higher force, ideal for thicker metals or tougher rivets but tend to be pricier and less common for DIY.
- Air Pressure Tips: Keep air pressure within manufacturer specs to avoid over-compression or weak joints.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
- SizescURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. gloves cURL Too many subrequests.
- Use cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.

Preparation
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
Construction and Structural Uses
Rivets are common in building bridges, steel frames, and heavy structures. They handle stress and vibrations better than bolts in many cases. Plus, rivets won’t loosen over time like bolts might, making them ideal for long-lasting stability.
Automotive and Aerospace
In cars and planes, riveting holds together body panels, aircraft skins, and interior parts. Rivets help manage vibration and keep structural integrity even under stress, which is crucial for safety. Aerospace especially relies on rivets because they’re lightweight but super tough.
DIY and Crafting
If you’re into jewelry making, furniture, or small metal projects, rivets provide neat, cold connections without heat or glues. This controllable joining method keeps delicate materials safe while offering a clean finish.
Emerging Uses
Sustainability is driving new uses for metal riveting. Recyclable rivets and cold riveting techniques lower environmental impact, making this traditional method modern and eco-friendly. Industries focused on green manufacturing find these options valuable for reducing waste.
In short, metal riveting adapts well across construction, transport, hobbies, and sustainability efforts—making it a versatile choice for many U.S. users and industries today.
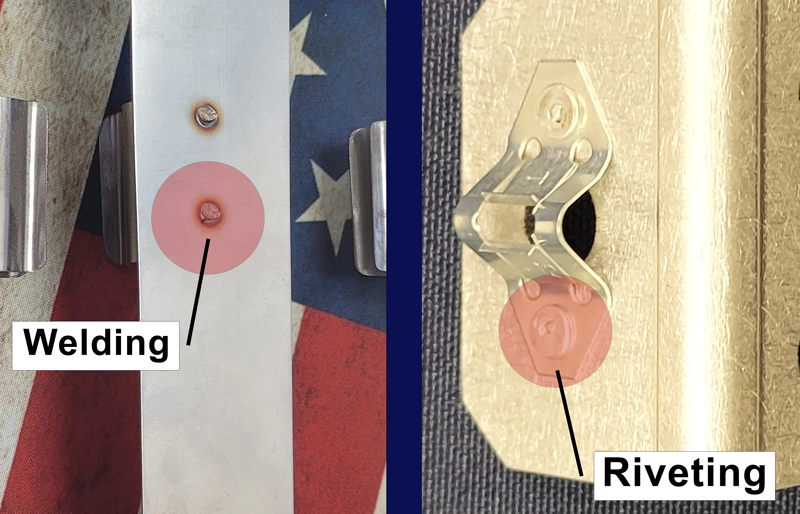
Advantages Disadvantages and Comparisons Riveting vs Welding and Beyond

When deciding between metal riveting, welding, or using screws, it helps to know the pros and cons of each method.
Pros of Metal Riveting
- Cost effective: Rivets and tools often cost less than welding gear or specialty fasteners.
- No heat distortion: Unlike welding, riveting doesn’t apply heat, so you avoid warping or weakening the metal.
- Easy inspection: You can quickly check if a rivet is properly set without special tools or testing.
Cons of Metal Riveting
- Permanent drilling: Holes are required for rivets, which are permanent and can’t be reused if you take the rivet out.
- Labor intensive: Setting rivets, especially solid ones, takes time and some skill compared to faster screw installation.
Head-to-head Riveting vs Welding vs Screws
- Riveting works best for joining dissimilar metals or thin sheets where heat is a concern, like in aircraft or automotive panels.
- Welding offers stronger joints for thick metals but requires more equipment and skilled operators. Heat can cause distortion or weaken certain metals.
- Screws are easiest for temporary or adjustable joints but don’t match the strength or vibration resistance of rivets or welds.
When to Choose Riveting
Consider riveting if your project:
- Involves thin metal sheets or delicate metals sensitive to heat
- Requires a long-lasting, vibration-resistant joint
- Needs quick inspection after installation
- You want a permanent yet cost-efficient metal joining method
If your work leans toward heavy fabrication or repair with thicker metals, welding might be better. For easy disassembly or less permanent connections, screws are the way to go. Use this quick decision path to pick the right metal joining technique for your project.
Common Mistakes in Metal Riveting and How to Avoid Them

When working with metal riveting, a few common mistakes can weaken your joints or cause problems. Here’s what to watch for and how to fix it:
Over-compression
- Too much pressure when setting rivets can cause cracking or split materials.
- How to avoid: Calibrate your rivet gun’s pressure settings before you start. Test on scrap metal to find the right force.
Misalignment
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- How to avoid: cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- How to avoid: cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests. and cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- Books: Look for “The Art of Metal Joining” and “Modern Riveting Techniques” for solid foundational knowledge.
- Forums: Reddit’s r/DIY and r/metalworking have active communities sharing tips and solving problems.
- Tutorials: Vast’s YouTube channel features beginner-friendly guides on how to install pop rivets and use proper riveting tools for DIY projects.
These resources help stay current with best practices, troubleshoot common issues, and explore new metal riveting trends.