Discover the die casting process for precision high-pressure metal moulding with aluminium and zinc alloys ideal for automotive and aerospace parts.
If you’re looking to manufacture high-precision metal parts efficiently, then understanding the die casting process—known in French as moulage sous pression—is essential. This method uses high-pressure injection to shape molten aluminium, zinc, or magnesium alloys into complex, durable components with tight tolerances and smooth finishes. Whether you’re an engineer, manufacturer, or procurement specialist, mastering die casting opens the door to faster production, cost savings, and unmatched repeatability. In this guide, we’ll break down the core principles, materials, applications, and design tips you need to optimise your next project with expert-level insight. Ready to take your manufacturing to the next level? Let’s dive in.
What Is Moulage Sous Pression A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Process Core Principles and How It Works
Moulage sous pression, or die casting, is a precise manufacturing process where molten metal is forced under high pressure into a steel mould, called a die. This technique allows for the fast production of complex metal parts with excellent surface finish and tight tolerances.
Here’s how it works step-by-step:
- Preparing the DieThe steel moulds are carefully designed and machined to match the desired part shape. These dies are built to withstand high pressure and repeated use.
- Melting the MetalCommon alloys like aluminium, zinc, or magnesium are melted in a furnace. The choice depends on the part’s strength, weight, and cost requirements.
- Injection into the DieMolten metal is injected into the die cavity at high pressure—hence “moulage sous pression.” This pressure ensures the metal fills every detail of the mould quickly and uniformly.
- Cooling and SolidifyingOnce injected, the metal cools rapidly inside the die, solidifying into the final shape. This speed reduces cycle time and helps maintain tight dimensional accuracy.
- EjectionAfter solidification, the die opens and ejector pins push the finished part out. The part is then ready for trimming and any necessary finishing steps.
Moulage sous pression is favoured because it combines speed, precision, and repeatability. It’s especially effective for producing high volumes of metal parts with complex shapes, such as automotive components, electronic housings, and aerospace fittings.
By understanding these core principles, you can see why die casting is a cornerstone of precision manufacturing and a top choice for many industries aiming for quality at scale.
Ready to explore how different types of moulage sous pression can fit your project? Let’s dive into the options next.
Types of Die Casting for Every Need

When it comes to moulage sous pression (die casting), choosing the right type depends on your project’s size, complexity, and material. The two main methods are hot-chamber and cold-chamber die casting.
- Hot-chamber die casting works best with low melting point metals like zinc and magnesium. The metal is melted and injected into the die using a built-in chamber, making it faster and perfect for small, detailed parts.
- Cold-chamber die casting handles metals with higher melting points such as aluminium alloys. Here, the molten metal is poured into a separate cold chamber before injection, offering better control for larger, thicker parts.
Other variations include:
- Squeeze casting, blending die casting and forging, useful for parts needing high strength.
- Vacuum die casting, which removes air bubbles ensuring better surface finish and fewer defects.
- Semi-solid die casting, injecting semi-solid metal to reduce porosity and shrinkage.
Knowing the right type means better precision, lower costs, and a finish that meets your expectations. Whether you need lightweight automotive metal parts or durable aerospace components, picking the right die casting method is key to success.
Key Materials in Die Casting Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project

Aluminium Die Casting Lightweight Powerhouse
When it comes to pressure casting, aluminium die casting stands out as a top choice, especially for projects that need strength and lightness. Aluminium alloys offer great durability without adding much weight, making them perfect for industries like automotive and electronics where reducing weight matters.
Here’s why aluminium die casting is a go-to:
- Lightweight but strongHelps improve fuel efficiency in cars and ease of handling in electronics
- Excellent corrosion resistanceKeeps parts lasting longer in harsh environments
- Good thermal conductivityIdeal for components that need heat dissipation
- Cost-effective productionAluminium alloys are cheaper than some alternatives while still delivering quality
- Precision friendlyWorks well with the high-pressure metal injection process to produce detailed parts
For UK manufacturers and custom moulding factories, aluminium die casting provides an excellent balance of performance and cost—perfect for scaling from prototypes to large production runs without compromising quality.
Key Materials in Die Casting Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project Zinc and Magnesium Alternatives
When it comes to moulage sous pression, Beyond aluminium, zinc and magnesium offer strong alternatives depending on your project needs. Both metals bring unique benefits that can be valuable in high-pressure metal injection processes.
Zinc Die Casting Advantages
- Excellent strength and durabilityZinc parts handle stress well, making them great for mechanical components.
- Fine detail and precisionZinc flows easily into die moulds, perfect for complex designs.
- Corrosion resistanceHelps parts last longer, especially in outdoor or humid environments.
- Cost-effectiveZinc alloys usually cost less than aluminium, which can save on production, especially for high-volume runs.
Magnesium Die Casting Advantages
- Lightweight: Magnesium is one of the lightest structural metals, ideal for components where reducing weight is important.
- Excellent strength-to-weight ratio: Provides robust parts without bulk, commonly used in automotive and electronics.
- Good thermal conductivity: Assists in applications requiring heat dissipation.
When to Choose Zinc or Magnesium
- Pick zinc for detailed, durable components that require good corrosion resistance at a lower cost.
- Go with magnesium when weight reduction is critical but you still need strength and heat management.
Both options are suitable for the precision manufacturing process of die casting, offering versatility to meet various project requirements. For UK customers aiming to balance quality, cost, and design complexity, considering these alloys alongside aluminium broadens your options in custom pressure casting solutions.
Key Materials in Die Casting Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project Material Selection Tips from Industry Experts
When it comes to moulage sous pression (die casting), selecting the right alloy is a game changer. Based on experience, here are some quick tips our experts recommend to help you choose the best material for your project:
- Understand Your Application: Different industries require different properties. For example, aerospace components need lightweight yet strong aluminium alloys, while automotive metal parts might prefer zinc for its excellent strength and corrosion resistance.
- Balance Cost and Performance: Aluminium alloys offer a great strength-to-weight ratio but can be more expensive. Zinc and magnesium are cost-effective yet rigid alternatives. Consider your budget without compromising on the specifications you need.
- Consider the Casting Process: Hot-chamber vs cold-chamber die casting can influence your material choice. Hot-chamber works well with low-melting-point metals like zinc, while cold-chamber suits aluminium and magnesium.
- Surface Finishing Matters: Some alloys accept surface finishing techniques better, so mind this during selection if your design needs that polished look.
- Consult Experts Early: Don’t wait until the final stages. Getting advice from die casting specialists, like those at vast custom moulding under pressure factories, can save time and avoid costly reworks.
Following these tips ensures your moulded parts meet quality and durability expectations without blowing your timeline or budget.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Die Casting Is It Right for You
Top Benefits for High-Volume Production
If you’re looking for moulage sous pression (die casting) to handle large-scale production, this method really shines. Here’s why it’s a go-to choice for many manufacturers in the United Kingdom:
- Fast Production Speed: Die casting uses high-pressure metal injection, meaning parts are created quickly and with consistent quality—perfect for keeping up with tight deadlines.
- High Precision and Detail: The die mould design ensures parts come out with excellent surface finishes and tight tolerances, reducing the need for extra machining.
- Cost-Effective at Scale: While initial setup costs can be high, producing thousands of parts drops the cost per unit significantly, making it ideal for large runs.
- Material Efficiency: Moulding under pressure minimises material waste compared to other methods, which boosts sustainability and cuts costs.
- Strong, Lightweight Parts: Using alloys like aluminium, zinc, or magnesium, die casting delivers parts that are durable yet lightweight—great for automotive metal parts and electronics.
- Versatility: Die casting can handle complex shapes and designs, which helps manufacturers meet diverse needs without sacrificing quality.
This process fits industries that demand consistent, high-quality parts in large quantities, such as automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods. If speed, precision manufacturing, and cost-efficiency in volume matter to you, die casting has your back.
Next, let’s look at some of the drawbacks and how you can address them before deciding if this method fits your project perfectly.
Potential Drawbacks and Mitigation Strategies
While moulage sous pression While die casting offers many benefits, it is not without its challenges. Understanding these potential drawbacks helps you decide if this high-pressure metal injection method suits your project, and how to address any issues.
Common Drawbacks: High Initial Costs
Setting up die casting requires expensive moulds and machines. This can be a barrier for small runs or prototype projects.
Limited Part Size
Large or very complex parts can be difficult or impossible to cast due to mould and machine limitations.
Porosity Issues
Air pockets or gas trapped inside can cause weak spots in parts—this affects strength and surface finish.
Design Restrictions
Some intricate shapes or thin walls may be difficult to produce reliably without mould redesign.
How to Mitigate These Drawbacks: Plan for Volume
Use die casting when you have medium to high production volumes to distribute the initial mould cost.
Choose the Right Machine
Hot-chamber for zinc or magnesium alloys, cold-chamber for aluminium—all improve quality and reduce porosity.
Work with Expert Mould Designers
Good die mould design is key. It helps avoid defects, reduce waste, and support complex geometries.
Post-Processing
Techniques like surface finishing and heat treatment can fix minor porosity and enhance part durability.
In the UK market, where reliability and finish quality are crucial, balancing these factors makes moulage sous pression a smart choice for many manufacturing needs. If you’re starting out, partner with a supplier or a custom pressure moulding factory that offers experience in these mitigation strategies. This ensures you get parts that meet your standards without hidden costs down the line.
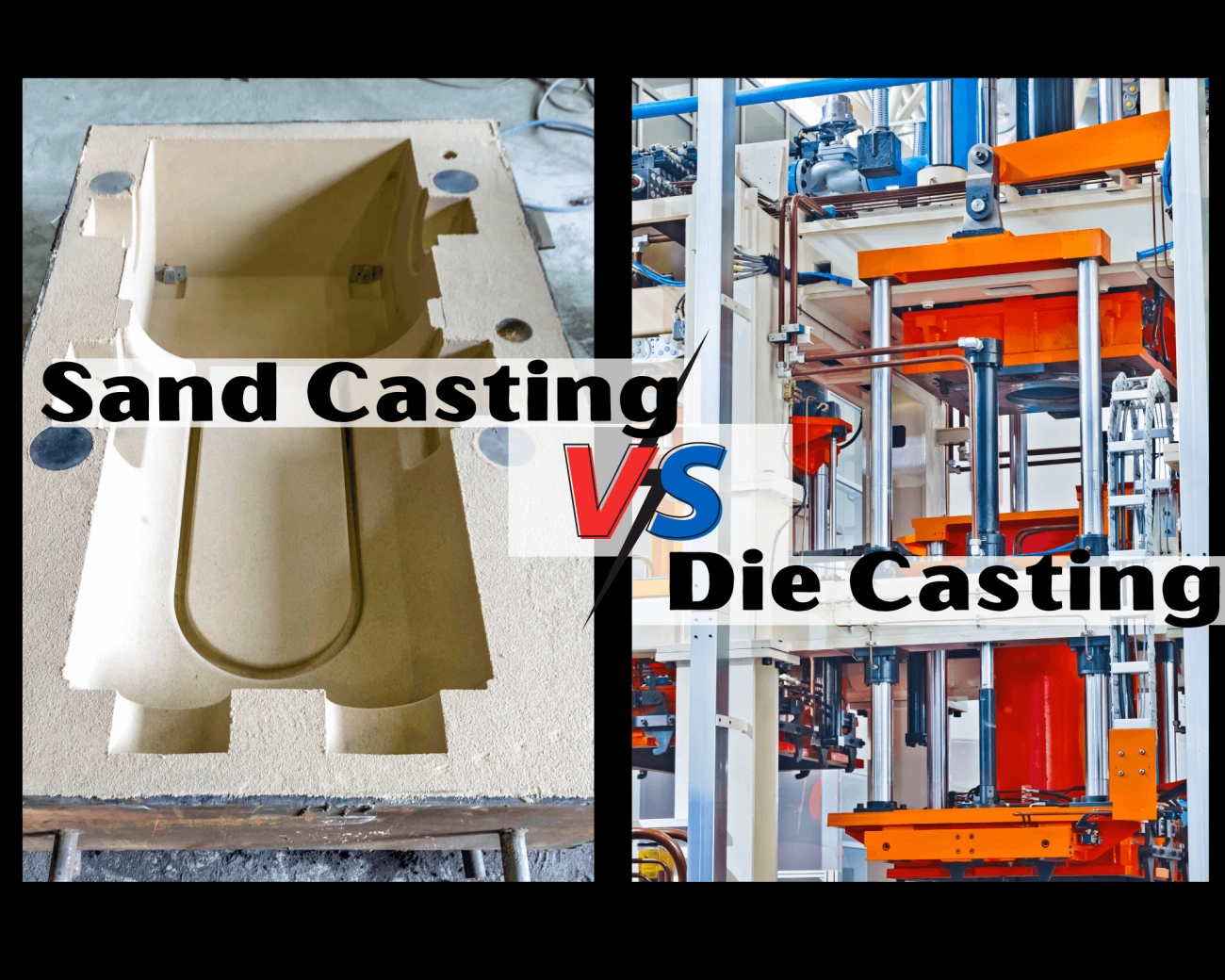
Die Casting vs Alternatives
When comparing moulage sous pression (die casting) against other metal forming methods, it’s important to understand what distinguishes it and when it might be the best choice for your project.
How Die Casting Stands Out
- High precision and repeatability: Die casting offers excellent dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes right off the mould, reducing the need for extra machining.
- Fast production rates: Perfect for high-volume runs, this process speeds up manufacturing without compromising quality.
- Complex shapes: It can easily produce intricate designs that might be tough or costly with methods like forging or machining.
- Cost-effective for large batches: Once the die mould is ready, cost per part drops significantly at scale.
Alternative Processes to Consider
- Sand casting: More flexible for low volume or very large parts but has rougher surface finish and less precision.
- Investment casting: Great for complex shapes and smaller volumes but slower and often pricier per part.
- Forging: Offers superior strength but limited in shaping complex geometries.
- Machining from solid stock: High precision but wasteful and expensive for large runs.
When Die Casting Might Not Be Ideal
- High initial tooling costs can be a drawback for smaller projects.
- Not suitable for very large parts due to size limits of moulds and machines.
- Some alloy choices are limited compared to other casting methods.
Quick Comparison
| Process | Best Use | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High-volume, detailed parts | Fast, precise, smooth finish | High tooling cost, size limit |
| Sand Casting | Large, low volume parts | Low tooling cost, flexible | Rough finish, less precise |
| Investment Casting | Complex, low volume parts | Good detail and surface | Slower, more expensive |
| Forging | Strong, simple shapes | High strength | Limited detail |
| Machining | Precision, prototyping | Accurate, no tooling | Expensive, slow for big runs |
Choosing moulage sous pression over these depends on your product’s volume, complexity, and budget. For many UK customers in automotive, electronics, and consumer goods, die casting hits the sweet spot with its balance of quality, speed, and cost. If you’re looking for a custom moulage sous pression China factory to partner with, it’s essential to evaluate these factors carefully to get the most value out of your investment.
Real-World Applications Die Casting in Action Across Industries Automotive and Transportation
When it comes to moulage sous pression (die casting), the automotive and transportation sectors are some of the biggest users. This high-pressure metal injection method delivers strong, lightweight parts that meet the demanding standards of vehicle manufacturing.
Why Die Casting Works Well in Automotive
- Strength and Precision: Die casting produces complex shapes with tight tolerances—perfect for engine components, transmission parts, and chassis elements.
- Lightweight Aluminium Alloy Casting: Many car manufacturers rely on aluminium die casting to reduce weight without sacrificing durability. Lighter vehicles mean better fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
- High Volume Efficiency: For automakers, rapid and cost-effective prototyping is essential. Moulage sous pression allows for quick production runs without compromising quality.
- Surface Finishing Techniques: Die-cast parts emerge with smooth surfaces, which reduces post-production finishing time and cost.
Common Automotive Components Made By Die Casting
- Engine blocks and cylinder heads
- Transmission housings
- Fuel system parts
- Brackets and supports
- Interior and exterior trim components
Benefits for Transportation Beyond Cars
- Die casting is vital for manufacturing parts in trains, buses, and trucks.
- Zinc die casting advantages include corrosion resistance suitable for parts exposed to harsh elements.
- Precision manufacturing process ensures safety-critical parts meet strict standards.
In the UK market, local manufacturers value custom moulage sous pression factories that can deliver consistent quality for both prototypes and large-scale production. This keeps supply chains tight and costs competitive while ensuring parts meet automotive industry demands.
Real-World Applications of Die Casting in Action Across Industries Aerospace and Electronics
Pressure die casting plays a critical role in aerospace and electronics, where precision and reliability matter most. In aerospace, lightweight aluminium alloy casting is a game-changer. It helps manufacturers create strong, yet lightweight parts that improve fuel efficiency and performance. Components like housings, brackets, and connectors benefit from high-pressure metal injection, providing tight tolerances and consistent strength.
In electronics, pressure die casting is essential for producing housings and heat sinks that protect sensitive components. Zinc die casting advantages include excellent electrical conductivity and precise surface finishing techniques, which help meet the stringent demands of consumer and industrial devices. Cold-chamber processes are often preferred here for their ability to handle metals like aluminium and zinc efficiently, ensuring top-tier quality in delicate parts.
For UK-based companies, working with a custom pressure die casting factory in China can offer cost-effective prototyping and scalable production options without compromising quality. This combination keeps projects on budget and schedule—two key factors in the fast-paced aerospace and electronics markets.
Real-World Applications Die Casting in Action Across Industries Emerging Uses in Consumer Goods and Renewables
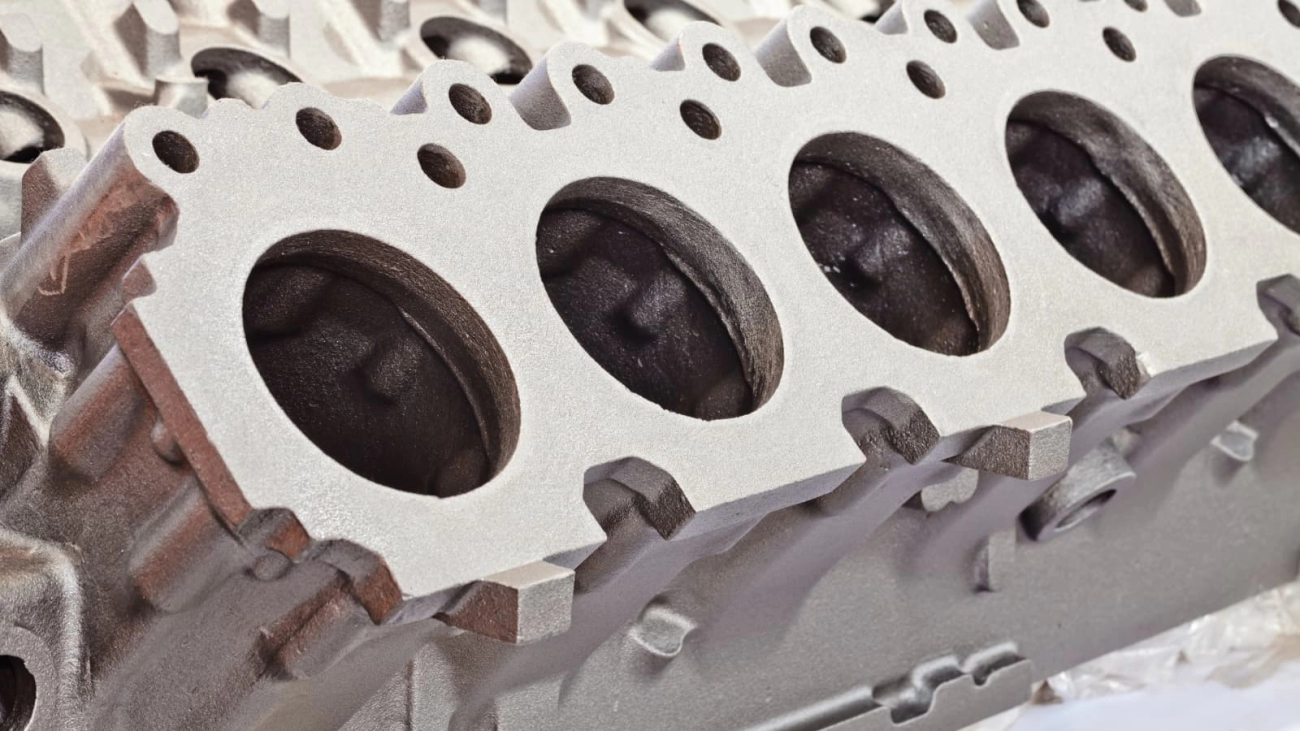
Pressure die casting (die casting) is gaining ground in consumer goods and renewable energy sectors because of its precision and cost-effectiveness. In consumer products, die casting helps create durable, lightweight metal parts for items like power tools, kitchen appliances, and electronics casings. These parts benefit from high-pressure metal injection, resulting in smooth finishes and strong components that can stand up to daily use.
In renewable energy, die casting plays a key role in manufacturing components for solar panels, wind turbines, and battery systems. Aluminium alloy casting is especially popular here because it combines strength with light weight, helping to improve efficiency and lower overall equipment weight. Manufacturers in the UK are choosing custom pressure die casting factories in China for scalable solutions that match growing clean energy demands while keeping costs down.
Key benefits in consumer goods and renewables include:
- Precision manufacturing process for consistently accurate parts
- Material versatility, especially with aluminium, zinc, and magnesium alloys
- Surface finishing techniques that improve corrosion resistance and appearance
- Cost-effective prototyping allowing quick development cycles
Using die casting in these emerging fields supports innovation and sustainability, making it a smart choice for businesses aiming to compete in today’s UK market.
Mould Design Essentials
When it comes to moulage sous pression, a well-designed mould is the foundation of a successful die casting project. A good mould ensures parts come out precise, consistent, and with minimal defects. Here are the essentials to keep in mind:
- Simple and Clear Flow PathsDesign the mould to allow molten metal to flow smoothly without turbulence. This reduces air pockets and ensures every detail fills correctly.
- Adequate VentingProper venting is crucial. It lets trapped air escape, avoiding defects like porosity or incomplete filling.
- Durable Materials for MouldUse hardened steel or other strong materials that withstand high pressure and repetitive cycles, ensuring the mould lasts.
- Consider Draft AnglesAdd slight angles to mould walls for easy part release. This saves time and avoids damage when ejecting parts.
- Balanced ThicknessKeep wall thickness uniform to prevent hot spots or cold seams, which can weaken the finished piece.
- Incorporate Cooling ChannelsProper cooling helps control the solidification process, improving part quality and reducing cycle times.
- Plan for Machining and FinishingDesign with any post-processing in mind, like surface finishing techniques, to simplify later steps.
In short, the right mould design directly impacts the quality and cost-efficiency of your die casting run. Prioritising these essentials helps deliver precise, high-volume parts that meet your standards.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Mould Pressure Casting Design
When designing parts for pressure casting, avoiding common mistakes can save you time and money. Here’s what to watch out for:
- Overly Complex ShapesKeep designs simple where possible. Complex shapes can cause defects like porosity and increase mould wear.
- Ignoring Draft AnglesAlways include draft angles to help with part ejection. Without them, parts may stick, damaging both mould and product.
- Thin Walls and Uneven ThicknessTry for consistent wall thickness to avoid shrinkage and warping. Ultra-thin walls may lead to incomplete filling.
- Sharp Corners and EdgesUse rounded corners instead of sharp angles. Sharp corners can cause stress concentrations and cracks.
- Insufficient VentingProper venting in the mould design prevents air traps and improves metal flow, reducing porosity.
- Wrong Material for ApplicationSelect alloys suited to your part’s function to ensure strength, corrosion resistance, and finish.
- Overlooking Surface Finishing NeedsPlan for surface finishing techniques early. Some die casting methods result in rougher surfaces needing extra work.
By steering clear of these usual pitfalls in your custom pressure casting design, you’ll end up with better quality metal parts that are easier and more cost-effective to produce. This approach fits well for UK manufacturers focusing on precision manufacturing and durable automotive metal parts.
Costs, Quality Control and Scaling with Vast
Breaking Down Die Casting Costs
When it comes to moulage sous pression, understanding the costs involved is key to making smart decisions for your project. Here’s a simple breakdown to help you see where your money goes:
- Tooling costsDesigning and building the die mould is the biggest upfront expense. It’s a custom piece made to fit your exact part, so expect an investment that pays off in the long run with repeatable precision.
- Material costsThe price depends on the alloy you choose—aluminium alloy casting tends to be more expensive than zinc or magnesium, but offers better strength-to-weight ratios.
- Production run sizeHigh-pressure metal injection shines when you produce in volume. The more parts you make, the lower the cost per piece, making it ideal for automotive metal parts or electronics.
- Machine operation and labourOperating cold-chamber or hot-chamber machines requires skilled labour and energy, influencing hourly costs. Automation can reduce labour costs over time.
- Finishing processesSurface finishing techniques like polishing or coating add extra costs but improve final part quality and aesthetics.
For UK manufacturers and buyers working with a custom moulage sous pression China factory, getting a clear quote that includes all these factors helps avoid surprises. It also makes budgeting for prototyping or scaling production smoother.
In short, high-volume projects benefit most from die casting’s cost structure, but it’s essential to weigh tooling and setup costs against expected yields. We work closely with clients to optimise every step, ensuring a balance of quality and cost-effectiveness.
Costs, Quality Control and Scaling with Vast
Ensuring Top-Tier Quality
When it comes to moulage sous pression (die casting), maintaining high quality is non-negotiable—especially for UK businesses relying on precision and consistency. Here’s how we ensure every part meets top-tier standards:
- Strict Quality Control ProcessesWe use advanced inspection methods throughout production, including dimensional checks and surface finishing verification. This helps catch issues early, ensuring parts match your specifications perfectly.
- Material TraceabilityTracking every batch of aluminium alloy casting or zinc components means no surprise in your final product. This attention to detail boosts reliability and performance in your applications.
- Consistent Die Mould DesignThe quality of your die moulds directly impacts accuracy and repeatability. We optimise die mould design for every project, reducing defects and enhancing the life of your tool.
- Surface Finishing TechniquesApplying the right finishing methods protects parts and improves aesthetics—critical for automotive metal parts and electronics where appearance and durability go hand in hand.
- Scalable Quality AssuranceWhether you need a few prototypes or full production runs, our scalable quality systems grow with your project. This makes cost-effective prototyping and volume production with consistent quality possible.
Choosing a trusted moulage sous pression factory with rigorous quality control keeps your supply chain smooth and reliable. When you work with partners who prioritize quality, your product stands out in the competitive market.
Scaling from Prototype to Production
Moving from a prototype to full production is a critical step in moulage sous pression. At Vast, we help businesses make this transition smoothly without compromising on quality or cost-efficiency.
When scaling up, here’s what you can expect:
- Consistent Quality: Our quality control in foundry processes ensure every part meets tight tolerances, so your parts look and perform exactly the same from the first run to the last.
- Optimised Die Mold Design: We refine the die mould design based on prototype feedback to reduce defects and speed up production.
- Cost-Effective Production: High-volume runs benefit from economies of scale, significantly cutting the cost per part compared to prototypes.
- Flexible Manufacturing: Whether you need aluminium alloy casting or zinc die casting, we customise the process to fit your industry needs—from automotive metal parts to electronics.
- Fast Turnaround: Our factory in China supports rapid tooling and production, helping UK-based businesses stay competitive.
By focusing on precision manufacturing processes and in-line quality checks, Vast ensures your move from prototype to full production is hassle-free and reliable.