Discover die casting process essentials including materials, benefits, and applications for precision high-pressure metal casting (moulage sous pression).
What Is Die Casting Understanding the Basics of Moulage Sous Pression
Die casting, known in French as moulage sous pression, is a manufacturing process where molten metal is injected at high pressure into a steel mould or die. This method allows for the creation of precise, complex metal parts with smooth surfaces and tight tolerances. The core principle behind moulage sous pression is using high pressure to force metal into every corner of the mould cavity, ensuring accuracy and repeatability that other casting methods often cannot match.
The process dates back to the early 19th century but really took off with the rise of industrial manufacturing and automotive industries in the 20th century. Innovations in mould design and metal alloys have driven its evolution, making it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
Today, die casting is key across many industries because it combines speed, detail, and material efficiency. Whether producing automotive die cast parts, electronic housings, or aerospace components, this technique delivers consistent quality and performance. Its role continues to grow, especially as manufacturers seek lightweight, strong components using aluminium die casting alloys and zinc alloy moulding to meet stringent industry standards.
The Die Casting Process Step by Step Breakdown

Understanding how moulage sous pression works is easier when you break it down into clear steps. Here’s a simple look at the process from start to finish, plus the main types of die casting you’ll come across.
Step 1 Mould Design and Preparation
The process starts with creating the die casting mould. This mould is usually made from steel and designed with extreme precision to match the final product’s shape. The design phase considers factors like manufacturing tolerances and cooling channels to ensure quality and efficiency. Once designed, the mould is carefully prepared and cleaned before use to avoid defects.
Step 2 Metal Melting and Injection
Next, the chosen metal alloy (like aluminium die casting alloys or zinc alloy moulding) is melted in a furnace. Depending on the type of die casting, the molten metal is injected into the mould using high pressure casting. The metal fills every cavity, producing detailed and precise metal parts.
Step 3 Cooling, Ejection, and Finishing
Once the metal cools and solidifies, the mould opens, and the cast part is ejected. After removal, the part undergoes finishing processes like trimming excess material, surface smoothing, or heat treatment to meet final specifications.
Types of Die Casting Hot Chamber vs Cold Chamber
- Hot Chamber Die Casting: The metal is melted inside the injection mechanism, making it ideal for low-melting-point alloys like zinc. It offers faster cycles and is common in automotive die cast parts and other precision metal components.
- Cold Chamber Die Casting: The metal is melted separately and then injected under pressure. This method suits high melting point metals like aluminium alloys and is widely used for tougher, larger parts.
Knowing these steps and types helps choose the right mould design and metal injection process for your project, especially when working with custom moulage sous pression solutions from trusted factories.
Materials in Die Casting Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Project
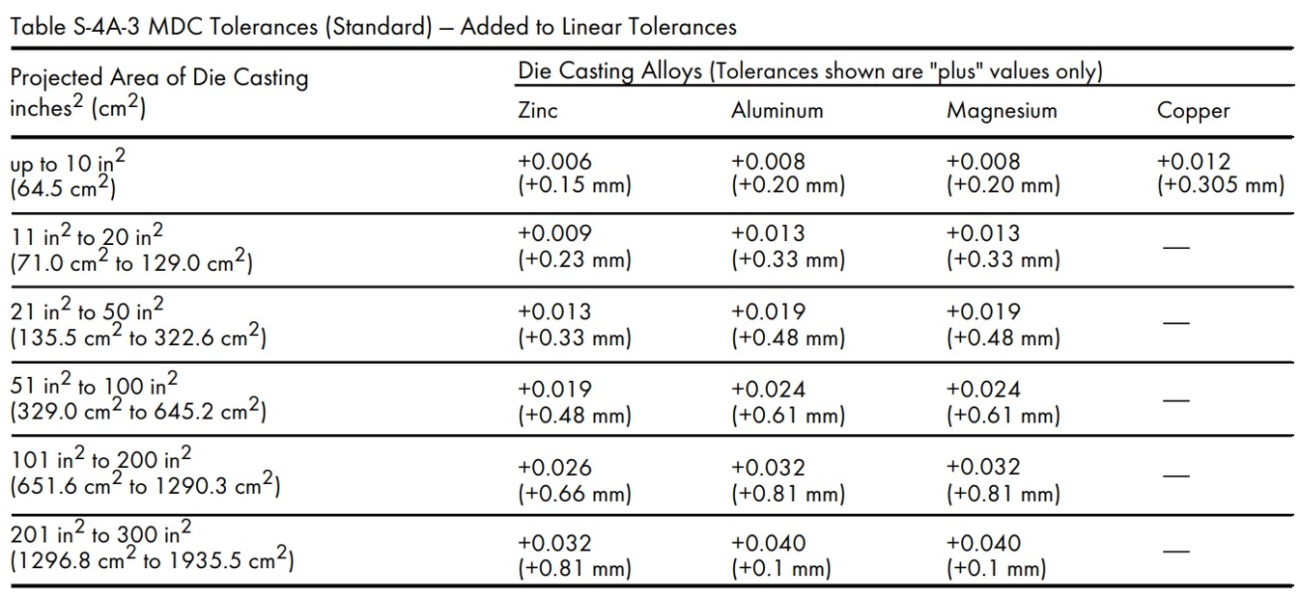
Selecting the right alloy for moulage sous pression is key to getting the best results for your project. Different metals offer different strengths, finishes, and cost points, so knowing what fits your needs helps avoid headaches down the line.
Common Alloys and Their Properties
- Aluminium Alloys Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and great for parts needing good thermal conductivity. Common in automotive and aerospace industries where weight matters.
- Zinc Alloys Ideal for high precision metal components. Zinc offers excellent strength and is perfect for complex shapes with tight manufacturing tolerances. It’s also good for fast machining and finishing.
- Magnesium Alloys Even lighter than aluminium, used where weight savings are critical, but it’s less common due to cost and handling considerations.
- Copper Alloys Used when high strength and electrical conductivity are required but not very common in high volume.
Material Selection Factors
When choosing an alloy, consider:
- Performance Requirements How strong, durable, or heat resistant does your part need to be?
- Cost Efficiency Budget constraints may influence whether you pick aluminium or zinc alloy moulding.
- Production Volume High-pressure casting runs favour alloys that cool quickly and can handle fast ejection for speed.
- Post Casting Finishing Techniques Some materials are easier to polish, paint, or machine after casting.
By matching your material choice to your project needs, you’ll optimise both performance and cost, ensuring your custom moulage sous pression delivers in the real world.
Applications of Moulage Sous Pression Across Industries

Die casting, or moulage sous pression, is a go-to process for many industries in the United Kingdom because it delivers precision metal components with consistent quality. Here’s where it really shines:
Automotive and Transportation
Automotive die cast parts are a huge part of this field. From engine blocks to transmission cases and structural components, high pressure casting with aluminium die casting alloys helps create lightweight, strong parts that improve vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Electronics and Consumer Goods
Die casting is perfect for making durable, detailed housings and connectors in consumer electronics. Zinc alloy moulding is especially popular here because it’s cost-effective and offers excellent finishing options, helping companies deliver sleek, reliable products.
Aerospace and Medical Devices
Precision and tight manufacturing tolerances are critical in aerospace and medical device parts. Moulding under pressure allows for complex shapes with high strength, ensuring that parts meet strict safety and performance standards without excess material or weight.
Real World Case Study Vast’s Custom Die Cast Solution for EV Components
An example from a leading factory shows just how valuable custom moulding under pressure can be. Vast, a United Kingdom-based company, developed a tailored die casting solution for electric vehicle (EV) components. Using aluminium die casting alloys and advanced metal injection processes, they produced lightweight, durable parts that improve battery housing and motor efficiency while cutting costs and lead times.
This kind of application proves that moulding under pressure isn’t just versatile; it’s essential for modern manufacturing across the board.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Moulding Under Pressure
Key Benefits
Moulding under pressure, or die casting, offers some strong advantages that British manufacturers value:
- High precision and consistency: This process delivers tight manufacturing tolerances, making it perfect for producing precision metal components repeatedly.
- Fast production times: Once the die casting mould design is set, you can produce parts quickly, helping meet high demand.
- Excellent surface finish: Little need for post casting finishing techniques, which saves time and cost.
- Strong and lightweight parts: Using aluminium die casting alloys or zinc alloy moulding, you get durable but lightweight automotive die cast parts and electronics housings.
- Cost-effective for large runs: Though initial tooling can be pricey, unit costs drop significantly with volume, especially in the custom moulding under pressure factories in China.
Potential Drawbacks and Mitigation Strategies
Like any process, die casting has downsides to keep in mind:
- High initial tooling costCreating the mould is expensive. To mitigate, plan for large production runs or prototype with cheaper methods first.
- Design limitationsComplex or extremely thin parts might be challenging. Work closely with mould designers to stay within best die casting mould design guidelines.
- Porosity issuesTrapped air can cause weak spots in parts. Using proper venting and metal injection process controls helps reduce this risk.
- Material restrictionsNot all metals suit die casting well. Selecting the right alloy carefully is essential for strength and corrosion resistance.
- Size limitsVery large parts may not be practical for this method, so consider alternative manufacturing if your project demands big components.
Being aware of these will help you maximise the advantages of pressure casting while avoiding common pitfalls in your United Kingdom-based projects.
Cost Factors and Optimisation Tips for Die Casting Projects
When planning a moulage sous pression project, understanding the costs involved is essential. Here’s a quick breakdown of what affects your budget and how you can save without cutting corners.
Breaking Down Expenses
- Mould design and manufacturingThis is typically the largest upfront cost. Complex mould designs increase the price but can improve efficiency later.
- Material costsChoosing the right alloy like aluminium die casting alloys or zinc alloy moulding can impact expenses.
- Production volumeHigher volumes usually mean lower per-piece costs due to economies of scale.
- Machine time and labour: The complexity of parts and cycle time affects how long machines run and labour hours.
- Post casting finishing techniques: Surface treatments, machining, or assembly add to overall costs.
How to Reduce Costs Without Sacrificing Quality
- Optimise mould design: Work with your supplier to simplify the design where possible, reducing machining time and tooling complexity.
- Select cost-effective alloys: Aluminium and zinc alloys balance performance and price well.
- Plan for volume: Faster production runs help amortise mould costs.
- Automate finishing: Using automated trimming or surface finishing can cut labour costs.
- Partner with experienced factories: Choosing a reliable custom moulage sous pression China factory can give you access to advanced tech and pricing benefits.
By focusing on these areas, you can keep your die casting project cost-effective while maintaining the precision and durability your applications require.