Explore torsion snap joint design principles, mechanics, and applications for durable, tool-free plastic fastening solutions.
If you’re working with plastic assemblies or precision fastening, understanding torsion snap joints can transform how you design quick, secure connections without tools. These clever rotational fasteners offer a smart alternative to traditional snap fits, delivering durability and ease of use that engineers and product designers crave. In this post, you’ll discover exactly how torsion snap joints work, their design essentials, and why mastering them can save time and cost in everything from consumer electronics to automotive panels. Ready to unlock smarter assembly solutions? Let’s dive in.
Core Mechanics How Torsion Snap Joints Work
Ever wondered how a torsion snap joint holds parts firmly yet lets you separate them when needed? The magic lies in twisting or torsional deflection. Unlike bending, these joints use a hinged arm or bar that rotates slightly to snap into place, creating a secure but reversible lock.
Fundamental Principles
At the heart of a torsion snap joint is a rocker arm or a torsion bar that acts like a tiny seesaw. When you push two parts together, the arm twists around its hinge shaft, applying torque and snapping a hook into a matching recess on the other part. Once snapped in, the joint resists pullout through elastic recovery—it wants to snap back, holding tight. When you want to separate the pieces, applying force causes the arm to twist back and release the hook.
Key Components
- Rocker arm: The twisting element that moves to snap the joint.
- Torsion bar/shaft: The hinge axis allowing rotational movement.
- Hook: The locking projection on the rocker arm.
- Mating recess: The slot or pocket where the hook snaps in.
They work together seamlessly to create a rotational snap fit that doesn’t rely on bending but on twisting motion.
Physics Behind the Snap
- Torque application: Force applied causes the arm to rotate about the hinge.
- Elastic recovery: Like a spring, the arm stores energy and pushes back to keep the hook engaged.
- Seesaw mechanism: The arm pivots on a shaft acting as a fulcrum, balancing forces during engagement and disengagement.
Quick Comparison Table: Torsion vs Other Snap Fits
| Feature | Torsion Snap Joint | Cantilever Snap Fit | Annular (Circumferential) Snap |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motion type | Rotational (twisting) | Linear bending | Radial expansion/contraction |
| Key stress | Torsional stress (twisting) | Bending stress | Compression/expansion |
| Typical components | Rocker arm, torsion bar | Flexible beam/tab | Circular groove and lip |
| Application | Hinges, clips needing rotation | Snap-on covers, simple locks | Ring seals, connector locks |
| Wear resistance | High fatigue life | Moderate | Variable |
Understanding how these core mechanics work makes it clear why torsion snap joints are a go-to for durable, user-friendly, space-saving interlocks.
Design Essentials Engineering Torsion Snap Joints for Reliability
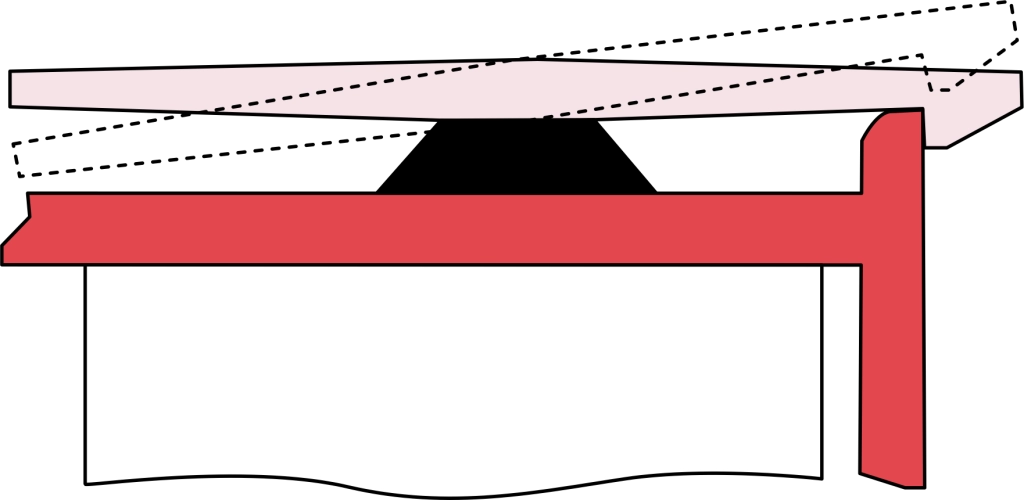
When designing a Torsion snap joint (扭转卡扣接头), choosing the right materials is key. For flexibility, polypropylene is a solid choice, while nylon stands out for its excellent fatigue resistance. Keep in mind factors like the material’s modulus and shrinkage—they impact how your snap joint performs over time.
Geometric Guidelines
- Arm length and hinge thickness: Longer arms increase flexibility but reduce strength, while thicker hinges add durability but limit rotation.
- Undercut angles: Aim for an entry angle under 45 degrees to make assembly easier.
- Exit angle: Keep it around 5 degrees to ensure a firm hold yet allow for easy removal without damage.
Stress and Deflection Calculations
Understanding the forces on your torsion bar helps prevent failures. Use these simple formulas to estimate maximum strain and deflection:
- Maximum strain = (hinge thickness / arm length) × applied torque
- Deflection force depends on arm length, hinge thickness, and material modulus
Step-by-step examples are useful here—start by calculating the torque needed for your application, then confirm your design stays within safe deflection limits.
Tolerance and Prototyping Tips
Moulding variations are part of production. To ensure your torsion snap joint fits well every time:
- Account for shrinkage and warpage during design.
- Use finite element analysis (FEA) simulations to spot stress points and tweak geometry early.
- Prototype with 3D printing or short-run moulding before scaling up.
These steps help build reliable torsion snap fits that meet performance expectations consistently.
Advantages and Limitations Weighing Torsion Snap Fits in Product Development

When designing with torsion snap joints (扭转卡扣接头), it’s important to know what they bring to the table—and where they fall short.
Advantages
- High retention force: These joints hold parts securely, making them great for products that need reliable fastening.
- Fatigue resistance: Thanks to their torsion bar design, they handle repeated use well without breaking down.
- Space efficiency: They provide rotational access in tight spaces where other fasteners might not fit.
- No tools needed: Assembly and disassembly are fast and tool-free, saving time on the production floor and during repairs.
- Assembly time savings: Quick snap-in and release reduce manufacturing and maintenance time, improving overall efficiency.
Limitations
- Stress concentrations at hinges: The hinge areas can see high stress, which might cause early failure if not designed or material-chosen properly.
- Misalignment sensitivity: Precise manufacturing is key, as small misalignments can cause jamming or failure of the snap joint.
- Limited for high load or permanent joins: These joints aren’t ideal for applications requiring super-strong, permanent bonds.
Mitigation Strategies
- Add fillets or rounded edges at hinge points to reduce stress.
- Use tougher materials like nylon for better fatigue resistance.
- Design for easy alignment with proper undercut angles.
- Consider secondary fastening methods if permanent strength is critical.
When to Choose Torsion Snap Joints
They work best for separable connections in compact designs where ease of assembly and repeated opening is important. Think battery covers, access panels, or light-duty clips.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Strong retention with flexibility | Stress at hinges |
| Handles repeated use well | Needs tight manufacturing tolerance |
| Saves space and assembly time | Not suitable for heavy permanent loads |
| No tools required | Sensitive to misalignment |
Understanding these trade-offs helps you decide if torsion snap fits suit your project needs in the United Kingdom market or any industry aiming for reliable, quick, and tool-free assembly.
Real World Applications of Torsion Snap Joints Across Industries
Torsion snap joints, or 扭转卡扣接头, are everywhere in products we use daily, thanks to their ease of use and reliable performance.
Automotive
You’ll find torsion snap joints in dashboard clips and interior panels. They hold parts firmly while absorbing vibrations, which helps reduce rattles and keeps everything in place during driving.
Consumer Electronics
Battery covers, device housings, and access doors often use torsion snap fits. They let users open and close parts easily without needing tools, making repairs or battery changes hassle-free.
Medical Devices
In medical tools and disposable assemblies, these joints offer quick assembly and disassembly, helping with sterility and fast tool changes in critical environments.
Case Study: Vast Toy Hinge Optimisation
Our team at Vast worked on a toy hinge using torsion snap joints designed for over one million cycles. We improved the hinge’s lifespan while keeping the snap action smooth and reliable, even after extended use. Visual tests confirmed durable performance with minimal wear—a big win for durability and user satisfaction.
Torsion snap joints really shine when you need reliable, user-friendly fastening across industries from cars to consumer gadgets and medical gear.
Best Practices and Common Pitfalls Avoid Design Failures
When designing torsion snap joints (扭转卡扣接头), following best practices is crucial to ensure reliability and avoid costly mistakes. Here are key tips to optimise your design:
Optimisation Techniques
- Fillet the roots of the hinge area to reduce stress concentrations and prevent early cracking. Sharp corners are a common failure point.
- Use iterative testing to validate cycle life. Aim for over 10,000 engagement cycles in your prototypes to confirm durability and fatigue resistance.
Manufacturing Integration
- Make sure your design suits injection moulding processes. Proper draft angles and uniform thickness help avoid warping or sink marks.
- For early-stage development, use 3D printing to quickly iterate and test torsion snap fit designs before committing to tooling.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Watch out for creep—permanent deformation under continuous stress—which can cause your snap joint to lose retention over time. Selecting materials like nylon with good fatigue resistance helps here.
- Consider environmental factors such as UV exposure and temperature extremes that may degrade plastics and reduce joint performance. Add stabilisers or protective coatings if needed.
Sustainability Considerations
- Torsion snap joints eliminate the need for extra fasteners like screws or rivets, reducing waste and assembly complexity.
- Implementing snap fits aligns well with eco-friendly design goals by lowering material use and enabling easier part recycling or disassembly.
By applying these best practices and watching out for typical pitfalls, you can create torsion snap joints that are both durable and efficient, meeting the high standards required by today’s UK market.
Vast expertise elevates your torsion snap joint projects
At Vast, we specialise in custom moulding services that take your torsion snap joint projects to the next level. Our team understands the unique challenges of designing and manufacturing reliable torsion snap fits, ensuring every piece delivers high performance and durability. Whether you’re working with polypropylene for flexibility or nylon for fatigue resistance, we tailor solutions that fit your product needs perfectly.
We offer a free design consultation to help refine your concept and avoid costly mistakes early on. Plus, our downloadable torsion snap joint calculator tool makes it easy to estimate stress, deflection, and force, helping you optimise your design before production.
Looking ahead, Vast is embracing future trends by integrating smart materials and AI-based geometry optimisation. This means your torsion snap joints will not only perform better but also adapt to evolving product demands, reducing development time and enhancing sustainability.
Partner with Vast to get precise, tested, and market-ready torsion snap joints that stand out in the UK market.