Discover X4CrNiMo16-5-1 martensitic stainless steel with high strength corrosion resistance and excellent weldability for demanding industrial applications.
Chemical Composition and Microstructure
X4CrNiMo16-5-1, also known as 1.4418 stainless steel, is a low carbon martensitic stainless alloy designed for high strength and corrosion resistance. Its balanced chemical composition includes:
| Element | Content (wt%) | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium | 15.5 – 16.5 | Provides corrosion resistance and hardenability |
| Nickel | 4.5 – 5.5 | Enhances toughness and improves corrosion resistance |
| Molybdenum | 0.8 – 1.2 | Boosts pitting corrosion resistance |
| Carbon | ≤ 0.03 | Controls hardness and martensitic transformation |
| Manganese | ≤ 1.0 | Deoxidiser and strength contributor |
| Silicon | ≤ 1.0 | Strengthens and aids oxidation resistance |
This alloy’s microstructure is predominantly tempered martensite, a phase formed through controlled cooling that offers a fine balance between hardness and toughness. Martensitic transformation imparts excellent mechanical strength, while tempering reduces brittleness by allowing controlled carbide precipitation.
Compared to standard 400-series martensitic stainless steels, such as X46Cr13 (1.4034), X4CrNiMo16-5-1 distinguishes itself with added nickel and molybdenum. These elements enhance corrosion resistance, especially in chloride-rich environments, and improve toughness significantly. This makes it a preferred choice where both high strength and moderate corrosion resistance are critical.
The tempered martensitic phase ensures improved impact behaviour under low temperatures, setting X4CrNiMo16-5-1 apart from typical 400-series grades which tend to be more brittle. This makes the alloy suitable for demanding industrial applications requiring reliable performance in harsh service conditions.
Mechanical and Physical Properties of X4CrNiMo16-5-1 Martensitic Stainless Steel
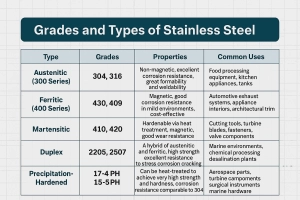
X4CrNiMo16-5-1, also known as 1.4418 stainless steel, offers impressive mechanical strength with tensile strength typically ranging from 850 to 1100 MPa and yield strength between 600 to 850 MPa, meeting EN 10088-3 standards. This makes it a solid choice for applications needing high strength without sacrificing toughness.
When it comes to hardness, it usually falls in the range of 280 to 360 HV, depending on heat treatment. What sets this martensitic stainless steel apart is its good toughness, even at low temperatures—offering reliable cryogenic ductility that many 400-series steels can’t match.
On the thermal and electrical side, X4CrNiMo16-5-1 behaves like typical martensitic steels, with moderate thermal conductivity and electrical resistivity. It’s not designed for high electrical or thermal insulation but performs well under varying temperature conditions.
Here’s a quick comparison with common austenitic grades like 304 and 316 stainless steels to highlight its mechanical edge:
| Property | X4CrNiMo16-5-1 (1.4418) | 304 Austenitic | 316 Austenitic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 850 – 1100 | 520 – 750 | 520 – 750 |
| Yield strength (MPa) | 600 – 850 | 210 – 275 | 240 – 290 |
| Hardness (HV) | 280 – 360 | 150 – 200 | 150 – 210 |
| Cryogenic Toughness | Good | Excellent | Excellent |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate (~20 W/m·K) | Lower (~16 W/m·K) | Lower (~16 W/m·K) |
| Electrical Resistivity | Moderate | Low | Low |
For industries in the United Kingdom requiring strong, durable materials—whether in energy, aerospace, or marine environments—X4CrNiMo16-5-1 delivers mechanical performance that remains resilient where others might bend.
Corrosion Resistance of X4CrNiMo16-5-1 Martensitic Stainless Steel

X4CrNiMo16-5-1 stainless steel offers solid corrosion resistance thanks to its balanced mix of chromium, nickel, and molybdenum. The chromium forms a protective oxide layer that shields the metal from rust, while molybdenum enhances resistance against pitting and crevice corrosion, especially important in harsh environments.
A useful way to measure this resistance is the Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number (PREN). This steel’s PREN typically ranges around 20-25, which is decent for martensitic grades but lower than some super austenitic steels. That means it performs well in moderately aggressive conditions but isn’t the top choice where extreme corrosion risk exists.
In seawater, X4CrNiMo16-5-1 withstands chloride attack reasonably well, making it suitable for marine and offshore equipment that encounter moderate salt exposure. It resists surface rusting and pitting but isn’t as durable as highly alloyed duplex or austenitic stainless steels in prolonged underwater use.
When it comes to acidic environments, this steel tolerates mild acids like dilute sulphuric or acetic acid, but it can corrode under strong acids or highly oxidising conditions. For industrial processes involving harsh chemicals or frequent acid exposure, precipitation hardening stainless steels or higher alloyed grades might be better alternatives.
Limitations and alternatives:
- Not ideal for continuous exposure to strong chlorides or aggressive acids.
- Cryogenic or high-temperature corrosion resistance is moderate, not exceptional.
- Consider duplex or austenitic stainless steels for better corrosion resistance in seawater.
- Precipitation hardening stainless steels can offer superior corrosion resistance plus strength for special applications.
This balance of corrosion resistance with mechanical strength makes X4CrNiMo16-5-1 practical for many industrial uses where moderate corrosion and wear resistance are both needed.
Heat Treatment, Welding and Fabrication of X4CrNiMo16-5-1 Martensitic Stainless Steel
Heat Treatment Cycles
For X4CrNiMo16-5-1 stainless steel, proper heat treatment is key to unlocking its strength and toughness. The typical process includes:
- Austenitising: Heat to 1020–1050°C (1870–1920°F) and hold for 30 minutes to dissolve carbides.
- Quenching: Rapid cooling, usually in air or oil, to form martensite.
- Tempering: Reheat to 480–620°C (900–1150°F) for 1–2 hours to reduce brittleness and improve toughness.
This cycle balances hardness and ductility, ideal for parts needing wear resistance and structural integrity.
Welding Methods and Filler Recommendations
Welding X4CrNiMo16-5-1 requires care to avoid cracking and preserve properties:
- Use TIG (GTAW) or MIG (GMAW) with low hydrogen filler wires.
- Recommended fillers: matching martensitic stainless steel grades or austenitic stainless steel fillers like 308L for better toughness and corrosion resistance.
- Preheat the base metal to 150–200°C to minimise thermal stress.
- Post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) at 600°C for 1 hour restores weld zone hardness and reduces residual stresses.
Machining and Forming Tips
While X4CrNiMo16-5-1 offers good machinability among martensitic steels, follow these tips for best results:
- Use sharp, high-speed tools with plenty of coolant.
- Keep cutting speeds moderate to avoid work hardening.
- For forming, the steel should be annealed before shaping to reduce cracking risk.
- Avoid excessive bending; when necessary, use larger radii.
Processing Parameters Table
| Process | Parameter | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Austenitising | 1020–1050°C (1870–1920°F) | Hold for 30 minutes |
| Quenching | Air or oil cooling | Avoid slow cooling |
| Tempering | 480–620°C (900–1150°F) | 1–2 hours |
| Preheat for Welding | 150–200°C (300–390°F) | Reduces cracking risk |
| PWHT | ~600°C (1110°F) | 1 hour |
| Machining Speed | Moderate | Use sharp tools and coolant |
| Forming | Annealed condition preferred | Use gentle bends, larger radii |
Following these guidelines ensures that X4CrNiMo16-5-1 martensitic stainless steel performs reliably through fabrication and retains its high strength and corrosion resistance in service.
Applications and Case Studies of X4CrNiMo16-5-1 Martensitic Stainless Steel
X4CrNiMo16-5-1 martensitic stainless steel is widely used across heavy industries in the UK, thanks to its strong combination of corrosion resistance and high strength. You’ll often find it in energy sectors for turbine components and shafts, where durability under stress and exposure to harsh environments is critical. In aerospace, it’s favoured for landing gear parts and structural elements that demand toughness without excess weight.
In the marine In the industry, this steel is a go-to for seawater-exposed parts like propeller shafts and pump components, thanks to its solid resistance against seawater corrosion. Mining operations also rely on it for tools and wear-resistant equipment that perform well under abrasive and corrosive conditions.
A notable case study involves a European hydrofoil project where X4CrNiMo16-5-1 was selected for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, supporting high-speed marine travel with lower maintenance costs.
Looking ahead, this steel grade is gaining traction in cryogenic storage applications. Its martensitic microstructure offers improved toughness at very low temperatures, making it suitable for storing liquefied gases safely. Emerging trends also point toward its use in next-generation industrial turbines where resistance to both mechanical and environmental stress is essential.
In short, X4CrNiMo16-5-1 stands out in industries that require a tough, corrosion-resistant steel that performs consistently under demanding conditions.
Equivalents Standards and Sourcing
X4CrNiMo16-5-1 martensitic stainless steel, also known as 1.4418 stainless steel, aligns with several international standards. It’s comparable to grades like UNS S41600 in the United Kingdom and JIS SUS 630 in Japan. The European standard EN 10088-3 covers this alloy, ensuring you get consistent quality and performance. If you’re looking for alternatives, precipitation hardening stainless steels can sometimes substitute depending on strength and corrosion needs.
When sourcing X4CrNiMo16-5-1, working with established suppliers like Vast offers real advantages. They provide certified stock with full traceability, meeting ASTM and EN specifications. Plus, they maintain reliable inventory levels in the United Kingdom, reducing wait times and shipping costs. Many specialised mills and factories in China produce this alloy, so Vast’s network helps ensure fast delivery without compromising quality.
Certifications commonly available include ISO 9001 quality management and material test reports (MTRs) for mechanical and chemical properties. This makes X4CrNiMo16-5-1 from trusted sources a safe choice for demanding projects in energy, aerospace, and marine industries.