Explore galvanoplasty electroforming process techniques benefits and applications for precision metal coating and durable corrosion-resistant finishes.
If you’ve ever wondered how to create perfectly detailed metal parts or achieve flawless, durable coatings, electroforming—or galvanoplastia in Spanish—is your go-to process. This fascinating technique lets you build up metal layers with precision and control, transforming everything from delicate jewelry to high-tech aerospace components. Whether you’re a maker, engineer, or curious learner, understanding the electroforming process opens doors to innovation and craftsmanship like never before. Ready to dive into the world where metal grows atom by atom? Keep reading to unlock the secrets behind this powerful metal deposition method.
What Is Electroforming Demystifying the Basics The Core Definition and How It Differs from Electroplating
Have you ever wondered what exactly electroforming is and how it stands apart from electroplating? Both processes involve depositing metal onto a surface using an electrodeposition process, but they serve very different purposes.
Electroforming is a precise metal fabrication technique where a thick layer of metal is deposited onto a substrate or mandrel to create a standalone, self-supporting metal part. Think of it as building a metal shell that can later be separated from the original form to recreate intricate designs or shapes with great accuracy.
In contrast, electroplating involves coating an existing object with a thin layer of metal to improve its surface properties, such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or aesthetic appeal. The key difference is that electroplating enhances the original item’s surface, while electroforming produces a new metal part altogether.
By focusing on metal deposition techniques that allow the removal of the mandrel, electroforming enables precision metal molding in ways that electroplating simply cannot match. This difference makes electroforming ideal for applications requiring detailed metal components with complex shapes and durability.
In short, if electroplating is about surface finishing, electroforming is about creating metal parts from the ground up. Understanding this distinction can help you choose the right process for your project or product needs.
What Is Electroforming Demystifying the Basics A Brief History From 19th Century Printing to Todays Precision Tech
Electroforming, or galvanoplastia, started back in the 19th century as a way to reproduce detailed printing plates. It was an early metal deposition technique that helped mass-produce sharp images for newspapers and books. Fast forward to today, and this process has evolved into a high-precision electrochemical fabrication method used in advanced industries like aerospace and electronics.
Instead of just making printing plates, modern electroforming creates complex, lightweight metal parts with incredible detail and strength. We now prepare mandrels carefully, use electrodeposition to build up layers of metal like nickel, and apply corrosion-resistant coatings to ensure durability. What started as a simple method for printing has grown into a crucial, sustainable surface finishing technique shaping the tech and manufacturing landscape in the US and worldwide.
The Electroforming Process Step by Step Breakdown

Preparing the Mandrel The Foundation of Precision
The first step in galvanoplastia, or electroforming, is preparing the mandrel. Think of the mandrel as the base or mold around which metal will be deposited. It’s crucial because the final metal layer takes the exact shape and details of this form. A well-prepared mandrel ensures sharp features and accurate dimensions.
Here’s how mandrel preparation typically works:
- Material choice: Mandrels can be made of metal, plastic, or wax, depending on what you want to achieve.
- cURL Too many subrequests. The surface has to be spotless to allow even metal deposition. Any dirt or oil can cause defects.
- Surface treatment: Often, the mandrel gets coated with a thin release layer or separator. This makes it easier to remove the electroformed part without damage once the process is done.
- Conductivity: Since electrodeposition relies on passing electric current, the mandrel’s surface must be conductive or coated to conduct electricity effectively.
Preparing the mandrel right is the foundation of precision in electroforming. It directly impacts the quality of the metal layer built on top and the durability of the finished part. Without a properly prepared mandrel, even the best metal deposition techniques can fall short.
The Electroforming Process Step by Step Breakdown Immersion and Electrodeposition Where the Magic Happens
Once the mandrel is ready, it goes into the electroforming bath for immersion. This step is where the real magic begins. The mandrel, acting as a mold, is submerged in a solution rich in metal ions—nickel electroforming is common here due to its durability and precision.
During the electrodeposition process, an electric current passes through the solution, causing metal ions to deposit evenly on the mandrel’s surface. This builds up a precise, corrosion-resistant metal layer that matches every detail of the mandrel. The thickness can be controlled by adjusting the time and current, allowing for exact shaping.
This metal deposition technique is known for creating complex and fine features that traditional molding can’t easily replicate. It’s a clean, efficient method that delivers smooth, consistent layers—key for aerospace component manufacturing, jewelry plating applications, and precision metal molding in electronics and medical devices.
In short, immersion and electrodeposition combine to form a seamless metal shell, setting the foundation for a high-quality electroformed product.
The Electroforming Process Step by Step Breakdown Post Processing and Separation Finishing for Perfection

Once the electrodeposition process builds up the metal layer on the mandrel, the next crucial step is post processing and separation. This phase ensures the final product meets the highest standards of precision and durability.
Here’s what happens in post processing:
- Careful removal of the mandrel: Depending on the material used, the mandrel may dissolve, melt away, or be mechanically separated. This step reveals the thin metal shell created by electroforming.
- Surface finishing: The metal layer is often polished, buffed, or treated to enhance appearance and corrosion resistance. This might include adding corrosion resistant coatings or applying other sustainable surface finishing techniques to protect the part.
- Trimming and inspection: cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- Smooth replication of delicate patterns without damage
- Ability to form lightweight, durable decorative pieces
- Sustainable surface finishing reducing waste compared to traditional methods
- Versatility from costume jewelry to fine art sculptures
For designers and makers in the U.S., electroforming offers a perfect balance of craftsmanship and efficiency, making it easier than ever to produce standout, custom pieces that attract local customers looking for quality and creativity.
Key Applications Where Electroforming Shines in Industry and Beyond Electronics and Medical Micro Precision for Cutting Edge Tech
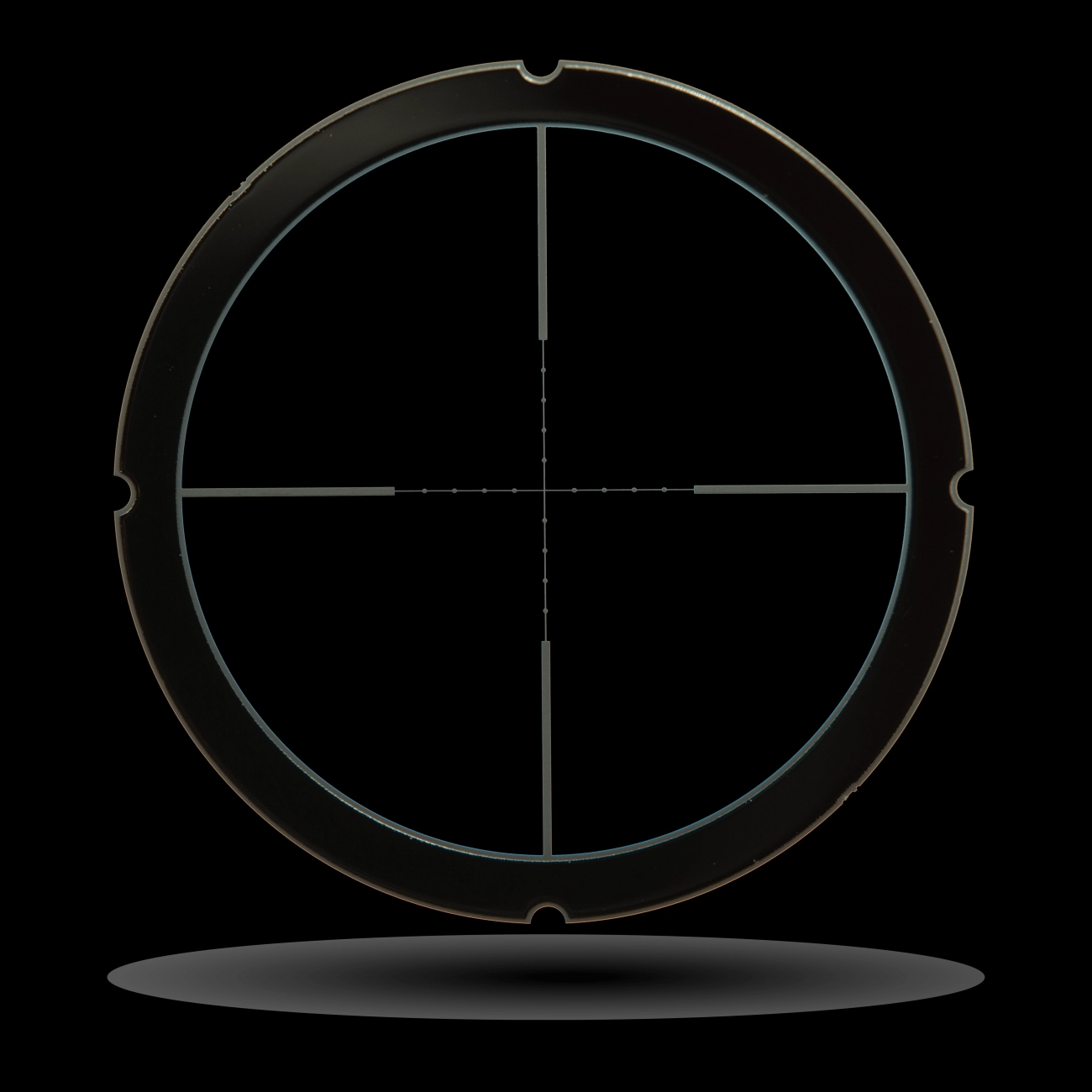

Electroforming plays a huge role in electronics and medical fields thanks to its ability to create super precise, tiny parts. The electrodeposition process in electroforming lets manufacturers build metal components with exact details on a small scale, which is perfect for today’s cutting edge tech.
In electronics, electroforming supports micro precision metal molding used in components like connectors, microchips, and circuit boards. The process excels at adding corrosion resistant coatings and conductive layers that are critical for performance and durability.
In medical devices, electroforming helps produce intricate parts for tools, implants, and diagnostic equipment. Nickel electroforming is popular here because it combines strength with biocompatibility, ensuring safety and long-lasting results.
Overall, electroforming gives industries the precision and reliability they need for micro metal components, making it a trusted method in US manufacturing for innovative electronic and medical products.
Benefits and Challenges Why Choose Electroforming Top Advantages Precision Scalability and Sustainability
Electroforming offers clear benefits that make it a smart choice for many industries, especially here in the U.S. Here’s why it stands out:
- Precision Metal Molding: Electroforming allows for extremely detailed and accurate metal parts, thanks to the electrodeposition process. This precision is hard to match with other metal deposition techniques, making it perfect for complex designs.
- Scalability: Whether you need a single prototype or a large production run, electroforming adapts well to different volumes. It’s flexible enough to support small jewelry batches or aerospace component manufacturing.
- cURL Too many subrequests.: Compared to traditional metal fabrication, electroforming produces less waste and uses materials more efficiently. This aligns well with growing demands for sustainable surface finishing in American manufacturing.
- Corrosion Resistant Coatings: The process can create durable, corrosion-resistant layers, which is ideal for industries like aerospace and automotive where metal longevity matters.
Electroforming combines these advantages with cost-effectiveness and the ability to replicate intricate shapes effortlessly, making it a solid option whether you’re customizing a unique piece or producing precision parts at scale.
Benefits and Challenges Why Choose Electroforming Common Challenges and How vast Overcomes Them
Electroforming has a lot going for it, but it’s not without its hurdles. Some of the common challenges include maintaining uniform thickness, avoiding defects like pitting or rough surfaces, and managing longer processing times compared to other metal deposition techniques. Precision is key, and slight mistakes during the electrodeposition process can cause issues in the final product.
Corrosion resistance and surface quality can also be tricky, especially with complex shapes or delicate mandrel preparation. Plus, scaling up from prototypes to full production sometimes brings unexpected challenges in consistency and cost control.
That’s where vast steps in. They use advanced controls during mandrel preparation and immersion to ensure smooth, uniform layers every time. Their expertise in nickel electroforming and other metal deposition techniques helps reduce defects and maintain precision. Plus, vast’s focus on sustainable surface finishing means they optimize processes to cut waste and energy use, which is a big win for U.S. manufacturers focused on both quality and environmental impact.
If you’re dealing with the common challenges of electroforming, vast’s technology and hands-on support make a big difference—helping you get consistent, high-quality results from prototype to full-scale production.
Getting Started with Electroforming Tips Tools and vast Expertise Essential Tools for Beginners and Pros
If you’re just diving into galvanoplastia (electroforming), having the right tools makes all the difference. Whether you’re a newbie or a seasoned pro, these essentials help you achieve precise metal deposition with ease and consistency.
Essential tools for starting your electroforming journey:
- Power Supply: A reliable DC power source controls the electrodeposition process, vital for building uniform metal layers.
- Electrolyte Bath: The solution where metal ions move and deposit; maintaining its quality ensures better results.
- Mandrels: These are the foundation shapes you coat. Proper mandrel preparation matters—a clean, smooth surface helps precision metal molding.
- Anodes: Usually made of the metal you want to deposit, like nickel for nickel electroforming; they maintain a steady metal supply in the bath.
- Agitation System: Keeps the electrolyte moving to prevent uneven coatings and speeds up deposition.
- Measuring Tools: Multimeters and thickness gauges help monitor voltage and coating thickness accurately.
- Safety Gear: Gloves, goggles, and good ventilation protect you from chemicals and electrical hazards.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.