Explore comprehensive insights on mold parts including components, functions, maintenance tips, and optimization for efficient injection molding processes.
The Anatomy of an Injection Mold: Core Components and Their Roles
Understanding the essential mold parts is key to mastering injection molding. Each component plays a specific role in creating high-quality parts with precision and efficiency. Let’s break down the core elements that make up a typical injection mold.
Mold Base and Structural Foundation
The mold base is the backbone of any injection mold. It provides a sturdy, aligned platform that holds all other components together securely. Usually made from hardened steel or aluminum, the mold base ensures durability and stability during the molding cycle. It also simplifies assembly and maintenance, acting as the foundation on which inserts, runners, and other parts are mounted.
Cavity and Core Inserts: The Heart of Part Formation
At the center of part manufacturing are the cavity and core inserts. These mold parts form the shape of the molded product by creating the hollow and solid spaces inside the mold. Precision mold inserts must be finely polished and engineered to exact tolerances to achieve detailed, defect-free parts. The cavity typically defines the outer surface, while the core forms the inner features — together shaping the final product.
Runner and Gating System: Ensuring Even Material Flow
The runner and gating system is like the mold’s circulatory system, guiding molten plastic from the injection nozzle into the cavity and core inserts evenly and efficiently. Proper runner design optimizes material flow and reduces waste, while gating placement minimizes turbulence and pressure drop, preventing defects like air traps or burn marks. Whether cold or hot runner systems are used, this network is critical for consistent part quality across production runs.
By mastering these core mold parts—the base, the inserts, and the flow systems—you set the stage for reliable, precise injection molding performance that meets today’s manufacturing demands.
Ejection and Guiding Mechanisms: Smooth Part Release Without Defects
In every quality injection mold, ejection and guiding mechanisms play a huge role in getting parts out clean and without damage. These mold parts work together to push the molded piece free and keep everything perfectly lined up.
Ejector Pins, Sleeves, and Plates: Pushing Parts Free
Ejector pins are the workhorses here. After the plastic cools and hardens, these pins push the finished part out of the mold cavity smoothly. Sleeves and plates support the pins, giving strength and stability. Together, they make sure the part doesn’t stick or warp during release, preventing common defects and keeping cycle times tight.
Guide Pins, Bushings, and Locating Rings: Precision Alignment
Guiding components keep the moving parts of the mold perfectly aligned each cycle. Guide pins slide right into bushings, holding everything on track and preventing misalignment. Locating rings help position the mold securely on the injection machine, which is key for consistent part quality. Without this precision, parts can come out banged up or poorly shaped.
Together, these ejection and guiding mold parts are essential for efficient production and defect-free injection molded parts, helping you make reliable products your customers expect.
Support Systems: Cooling, Venting, and Feeding for Optimal Performance
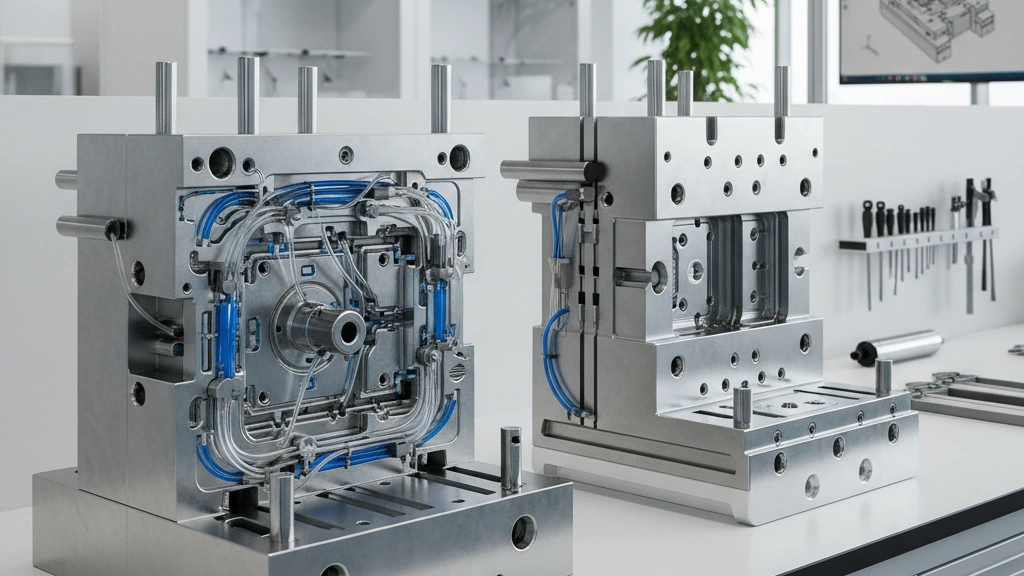
Proper support systems in mold parts are essential to keep production smooth and parts flawless. Here’s how cooling, venting, and feeding work together to optimize performance.
Cooling Channels and Baffles: Temperature Control Mastery
Cooling channels and baffles help control the mold’s temperature during injection molding. When the plastic melts and fills the mold cavity, it needs to cool evenly and quickly to maintain its shape and avoid warping.
- Cooling channels: These are pathways inside the mold parts where water or coolant flows to absorb heat.
- Baffles: Installed to direct coolant flow, ensuring consistent cooling across tricky spots.
Efficient cooling reduces cycle times and improves part quality, making your mold parts last longer.
Venting System: Avoiding Air Traps and Burn Marks
Venting is all about letting trapped air escape from cavities during molding. Without proper venting:
- Air pockets can cause burn marks or short shots (where the molten plastic doesn’t fully fill the cavity).
- Defects increase, and you risk damaging the mold or losing parts.
Small vents or venting grooves in mold inserts help cleanly release air, ensuring smooth plastic flow and defect-free parts.
Sprue and Feed System: From Machine to Mold
The sprue and feed system connects the injection molding machine to the mold cavity, guiding molten plastic where it’s needed. It includes:
- Sprue: The main channel where molten plastic enters the mold.
- Runner system: Distributes plastic evenly to multiple cavities when needed.
- Gate: Controls flow into each cavity, impacting part quality and cycle time.
Optimizing the runner and gating system in your mold parts ensures even material flow, reduces waste, and boosts efficiency on the shop floor.
Together, these support systems make sure your mold parts perform reliably, cut down cycle times, and maintain consistent part quality throughout production.
Material Selection and Customization: Tailoring Mold Parts to Your Needs
Choosing the right materials for your mold parts is key to getting reliable, long-lasting performance. Common materials like tool steel, aluminum, and stainless steel each bring different strengths to the table:
- Tool steel is tough and wear-resistant, great for high-volume runs and precision parts.
- Aluminio is lightweight and cools faster, perfect for prototypes or lower-volume projects.
- Stainless steel offers corrosion resistance, ideal for molds working with corrosive plastics or moist environments.
Deciding between custom and standard mold parts depends on your specific needs. Standard parts are cost-effective and quick to replace, but custom parts give you precise control over fit, finish, and performance. If your products demand tighter tolerances or unique design features, investing in custom parts tailored by experts like Vast can save time and reduce defects in the long run.
By carefully selecting and customizing your injection mold components, you ensure your molds run smoothly, produce high-quality parts, and meet the demands of U.S. manufacturing standards.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting: Extending Mold Life and Minimizing Downtime

Keeping your mold parts in top shape is key to avoiding costly downtime. Regular maintenance helps catch issues early and extends the life of your injection mold components.
Routine Inspection Protocols
- Check ejector pins and sleeves for wear or bending—these parts take a lot of stress.
- Inspect guide pins and bushings to ensure smooth alignment and avoid damage during mold cycles.
- Clean cooling channels and vents to prevent clogging, which can cause uneven cooling and defects.
- Look for signs of wear on cavity and core inserts, since precision mold inserts affect final part quality.
Common Failures and Fixes
- Ejector pins sticking or breaking: Often caused by dirt buildup or misalignment; clean and realign pins regularly.
- Runner system blockages: Clear out debris and consider hot runner systems to reduce material waste and clogging.
- Vent blockages: Lead to air traps and burn marks; maintain vents and avoid excessive mold temperature.
Upgrades with Vast Components
Investing in upgraded mold parts from suppliers like Vast can improve durability and precision. Advantages include:
- Custom-fit ejector systems designed to reduce sticking and damage.
- Enhanced cooling channel designs for consistent temperature control.
- High-quality guide pins and locating rings for better mold alignment.
Regular care combined with premium replacement parts keeps your molds running smoothly and your production line efficient.
Emerging Trends: Innovating Mold Parts for Tomorrow’s Manufacturing
The world of mold parts is evolving fast, and staying ahead means embracing new tech and smarter designs. Here’s what’s shaping the future of injection mold components:
Additive Manufacturing and Hybrid Molds
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, is changing how we make mold parts. It lets us create complex core and cavity inserts quickly and with less waste. Hybrid molds, which mix traditional metalwork with 3D printed parts, offer better customization and faster turnaround times. This approach is perfect for prototyping or low-volume runs here in the U.S., where flexibility and speed are key.
Smart Molds with IoT Integration
Smart molds are the next step. Embedding sensors into mold bases and runner systems lets manufacturers monitor temperature, pressure, and flow in real-time. That means fewer defects, better cooling channel control, and faster troubleshooting. For American factories aiming to boost efficiency, these IoT-powered molds can cut downtime and improve part quality.
Sustainable Innovations
With a growing focus on sustainability, mold parts now emphasize eco-friendly materials and energy-saving designs. Mold bases made from recycled steel or alloys improve longevity and reduce environmental impact. Optimizing runner and gating systems, including hot runner technologies, reduces plastic waste. This not only meets eco-conscious market demands but also lowers production costs over time.
Adopting these trends helps companies in the U.S. stay competitive, improve product quality, and support greener manufacturing practices. That’s the direction mold parts are headed—and it’s exciting.