Learn the polishing process with step-by-step guides on techniques, tools, and tips to achieve flawless mirror finishes on metals and more.
Ever stared at a dull metal piece and wondered how pros get that flawless, mirror-like finish? The polishing process is what transforms rough, scratched surfaces into smooth, shining works of art—and it’s not as complicated as you might think. Whether you’re polishing jewelry at home or refining parts in a small workshop, understanding the right steps, tools, and techniques can make all the difference. In this guide, you’ll discover how to master the polishing process to achieve stunning, durable finishes every time—no guesswork, just proven methods. Ready to unlock your project’s true shine? Let’s dive in.
Understanding the Fundamentals of the Polishing Process
Polishing is all about refining a surface by carefully removing material through friction. This process uses progressively finer abrasives—called grits—to gradually smooth out imperfections. Starting with coarser grits removes rough spots, while finer grits create a sleek, mirror-like finish. It’s a bit like sanding wood, but much more precise.
A key idea in polishing is how light interacts with the surface. Polished surfaces achieve specular reflection, meaning light bounces off evenly, giving that shiny, mirror-like look. In contrast, unpolished or rough surfaces scatter light in many directions, known as diffuse reflection, which makes them look dull. Proper surface preparation is essential to achieve this smooth reflection by eliminating scratches and irregularities.
There’s often confusion between polishing, grinding, and buffing. While all involve surface smoothing, grinding uses heavier abrasives to shape or remove significant material quickly, often leaving a rough finish. Buffing typically focuses on enhancing shine using soft wheels and compounds, usually after polishing has done the heavy work. Polishing sits in between, offering controlled material removal for a refined, defect-free surface.
By mastering these fundamentals, you set the stage for a successful polishing process, creating surfaces that not only look better but also perform better in their intended applications.
Types of Polishing Processes Choosing the Right Method for Your Needs
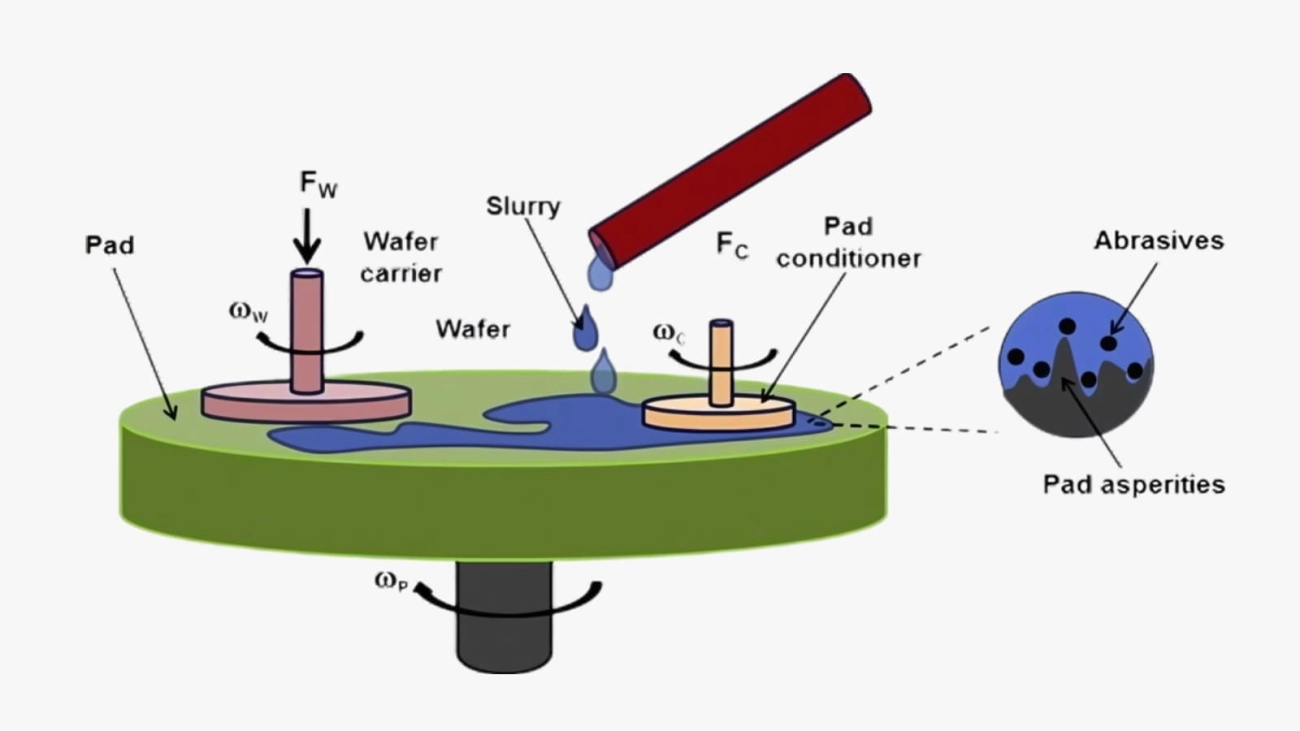
When it comes to polishing, choosing the right process depends on your material, budget, and desired finish. Here’s a quick look at the main types:
Mechanical Polishing Methods
- Hand Polishing: Great for small jobs and detailed work. Offers good control but takes more time and effort.
- Machine Polishing: Ideal for larger surfaces or high-volume work. Faster and more consistent, but requires equipment investment.
Both use abrasive polishing compounds to remove surface imperfections and create a smooth finish.
Chemical and Electropolishing Techniques
- Chemical Polishing: Uses chemical solutions to smooth surfaces by dissolving small amounts of material. Good for complex shapes but can be slow and involve hazardous chemicals.
- Electropolishing: An electrochemical process that removes microscopic layers for a bright, corrosion-resistant finish. Often used in medical devices and aerospace parts but requires precise control and equipment.
Other Polishing Variants
- Vibratory Polishing (Tumbling): Uses vibration and abrasive media to polish multiple small parts simultaneously. Efficient for batch processing but limited to smaller items.
- Chemical Mechanical Planarization (CMP): Common in electronics manufacturing to achieve ultra-smooth surfaces on wafers.
- Hybrid Approaches: Combining methods like mechanical grinding followed by electropolishing to balance productivity and quality.
Decision Framework
When picking a polishing process, consider:
- Material Type: Metals, plastics, glass, and ceramics respond differently to each method.
- Size and Scale: Large parts often need machine or chemical polishing, while small items might be better off hand-polished or vibratory polished.
- Cost and TimecURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
Pro tips for better polishing
- Use progressive grit jumping carefully. Don’t skip too many grit levels at once; it can cause surface damage instead of smoothing.
- Consider automation where possible. Machines can keep pressure and speed consistent, improving quality and saving time.
- Keep your abrasives clean and replace them regularly to avoid contamination and uneven polishing.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Over-polishing can wear away critical details and even cause heat buildup that damages the material.
- Applying inconsistent pressure leads to uneven finishes and can create defects like holograms or swirl marks.
- Rushing the stages skips vital surface preparation, impacting the final mirror finish.
Post-polish care and maintenance
- Apply protective coatings to preserve the polished surface and reduce corrosion risks, especially for metals.
- Perform routine inspections to catch early signs of wear, staining, or surface degradation.
- Clean surfaces properly after polishing to remove any residues that could affect appearance or performance.
Following these simple strategies will keep your polished parts looking great and performing well longer, which is essential whether you’re working with custom jobs from a polishing process factory in China or handling everyday polishing tasks locally.