Discover how plasma cutters work with expert insights on plasma arc cutting, key components, safety tips, and choosing the right system for precision metal fabrication.
What is Plasma The Science Behind the Spark
Ever wonder what plasma really is and why it plays a crucial role in cutting metals? Plasma is often called the fourth state of matter, joining solid, liquid, and gas. But unlike those familiar states, plasma is an ionized gas—meaning it’s made up of charged particles: ions and free electrons. This ionization happens when energy is added to a gas, stripping electrons from atoms and creating a super-hot, electrically conductive cloud.
The Four States of Matter Explained
- Solid: Atoms packed tightly in a fixed shape
- Liquid: Atoms flow but stick together
- Gas: Atoms spread out and move freely
- Plasma: Gas energized so much it becomes electrically charged and glows
This high-energy state allows plasma to conduct electricity and generate intense heat, essential for plasma arc cutting.
Why Plasma is Perfect for Cutting
Plasma’s unique qualities make it an ideal tool for metal cutting:
- It reaches temperatures up to 30,000°F, enough to melt most metals quickly
- The ionized gas forms a high-velocity plasma jet that blasts through the metal with precision
- Electrical conductivity lets it maintain a stable arc, enabling consistent cutting
- The heat is focused tightly, minimizing the surrounding material’s damage
This combination of heat and velocity means plasma cutters slice through tough metals cleanly and fast—perfect for everything from sheet metal projects to heavy industrial tasks.
Ready to see how this scientific spark turns into a powerful tool? Let’s break down the key components and step-by-step process next.
Key Components of a Plasma Cutter System
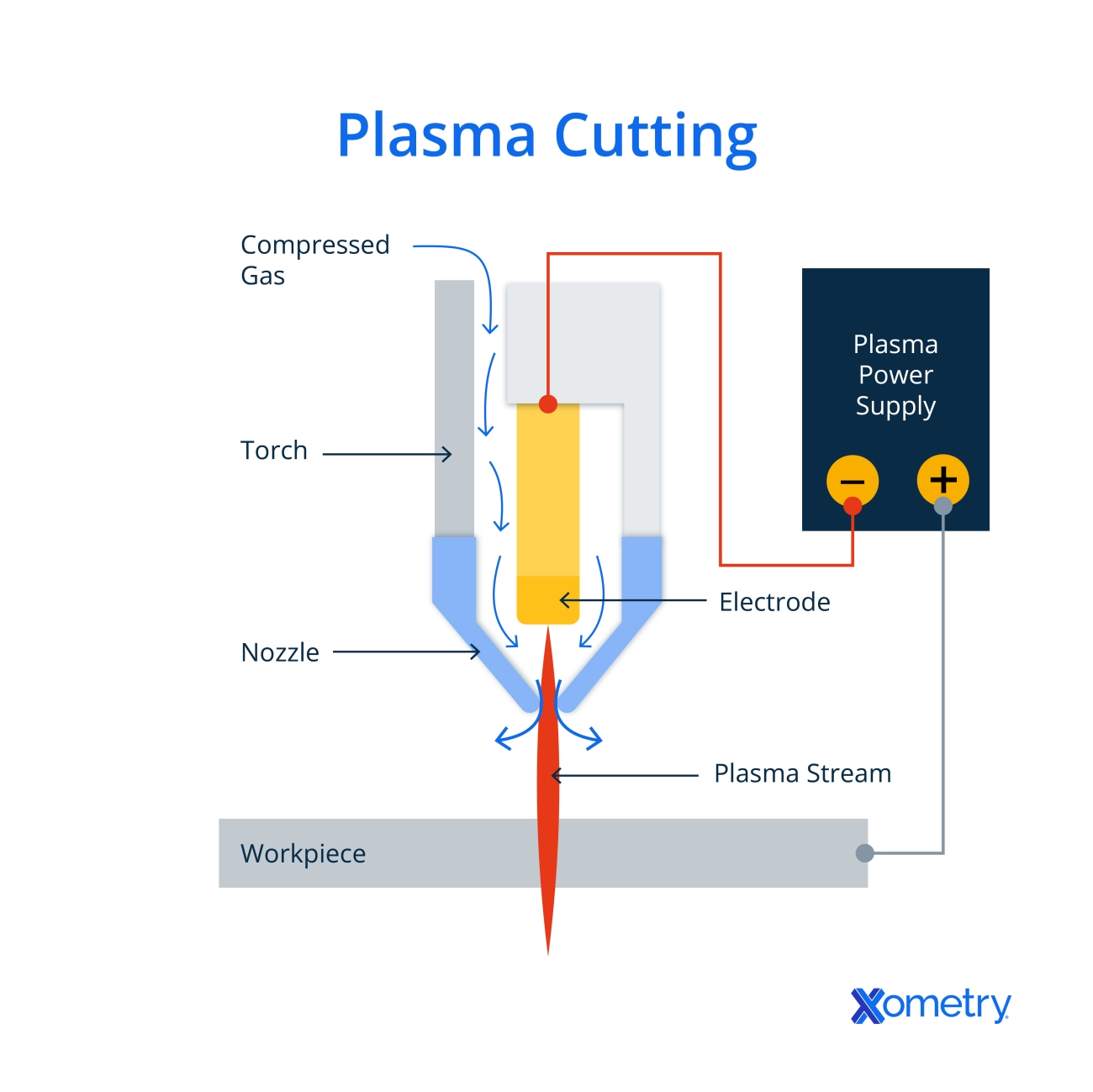
A plasma cutter depends on several key parts working together smoothly. Here’s a quick look at the main components:
Power Supply and Gas Delivery
The power supply is the heart of the system. It provides the high voltage and current needed to create the plasma arc. Along with power, the system needs gas—usually compressed air, nitrogen, or oxygen—to form the plasma. The gas delivery system controls the flow and pressure to keep the cutting process stable.
The Plasma Torch Electrode, Nozzle, and Swirl Ring
Inside the plasma torch, the electrode emits the electric arc that ionizes the gas. The nozzle shapes the plasma jet, focusing it for precision cutting. Around the nozzle, the swirl ring spins the gas so the plasma jet becomes tighter and hotter, which helps with cleaner and faster cuts.
Ground Clamp and Workpiece Setup
The ground clamp connects the plasma cutter to the metal piece you’re cutting. This completes the electric circuit required for the plasma arc to form. Properly setting up the workpiece and ground clamp ensures efficient cutting and safety by preventing arc instability.
Understanding these components helps you see how plasma arc cutting delivers powerful, precise cuts on metal. Each part plays a role in maintaining a strong, consistent plasma torch for your job.
Step-by-Step How a Plasma Cutter Actually Works
Step 1 Gas Pressurization and Arc Ignition
First, the plasma cutter powers up and pushes an inert gas—usually compressed air, nitrogen, or argon—through the torch. This gas gets pressurized tightly as it moves toward the nozzle. At the same time, the system creates an electric arc between the electrode inside the torch and the metal surface. This is called the pilot arc ignition. The electric arc heats the gas until it becomes ionized, turning into plasma—the super-hot, electrically charged gas that does the cutting.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- Handheld plasma cutters cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests. can create faster, cleaner cuts on steel by making the plasma hotter.
- Nitrogen and argon-mixes are best for cutting stainless steel and aluminum, helping reduce dross and improve edge quality.
Choosing the right combination depends on your material type, thickness, and precision needs. Knowing these basics helps you get the most out of your plasma arc cutting setup.
Real-World Applications and Advantages of Plasma Cutting

Plasma cutting is a go-to method in many U.S. industries because it’s fast, efficient, and handles a variety of metals well. Industries like construction, automotive repair, metal fabrication shops, and manufacturing rely heavily on plasma arc cutting for its precision and speed.
Industries Relying on Plasma Technology
- Construction and Structural Steel: Quick, clean cuts that fit tight project timelines.
- Automotive and Truck Repair: Easy to cut body panels and frames without warping.
- Metal Fabrication Shops: Precision sheet metal cutting for custom parts and designs.
- Manufacturing: High-volume cutting with CNC plasma systems improves productivity.
Key Benefits of Plasma Cutting
- Speed: Cuts through thick metals faster than traditional methods like oxy-fuel cutting.
- Precision: The high-velocity plasma jet allows for clean, accurate cuts with minimal dross.
- Versatility: Can cut stainless steel, aluminum, and other conductive metals up to several inches thick.
- Cost Savings: Less prep and cleanup, lower labor costs, and less wasted material.
Limitations and When to Choose Alternatives
- Material Thickness: For very thick metals, oxy-fuel cutting may be more cost-effective.
- Non-Conductive Materials: Plasma cutters only work on electrically conductive metals.
- Edge Finish: Though precise, plasma cutting may not match the finish quality of laser cutting for ultra-fine work.
In short, plasma cutting shines in jobs requiring speed and precision on conductive metals, especially when working with medium thicknesses. For specialized applications or very thick metal, other methods might fit better.
Safety Essentials and Best Practices for Plasma Cutting
When using a plasma cutter, safety is non-negotiable. Here’s what you need to keep in mind to stay protected and keep your workspace efficient.
PPE and Workspace Setup
- Wear proper PPE: Always use welding gloves, a flame-resistant jacket or apron, and a welding helmet with the right shade to protect against sparks and UV light.
- cURL Too many subrequests.: Use safety glasses under your helmet for added protection against flying debris.
- Good ventilation: Plasma cutting produces fumes, so work in a well-ventilated area or use fume extractors to keep the air clean.
- Clear work area: Remove any flammable materials and keep your workspace organized to avoid accidents.
- Ground clamp setup: Ensure the ground clamp is securely connected to the workpiece to prevent electrical shocks.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Poor cut quality: Check if your nozzle or electrode is worn out and replace if needed. Also, verify gas flow and pressure.
- Arc instabilitycURL Too many subrequests.
- OverheatingcURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
Factors to Consider
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.cURL Too many subrequests.
- PortabilitycURL Too many subrequests.
Top Recommendations from Vast
- VastPro 40: Great for small shop or hobby projects with up to 40 amps, easy to carry, and perfect for thin to medium metals.
- VastMax 60: Balances power and portability, great for professional use. Solid duty cycle for repeated cutting.
- VastX CNC Series: Best for those who want automated, precision sheet metal cutting. Perfect for fabrication shops needing CNC plasma.
Future Trends in Plasma Technology
- Smarter plasma cutters with better efficiency and longer consumable life.
- Increased use of inverter tech for lighter, portable designs.
- More integration with CNC and digital controls for precision and speed.
- Alternative gases improving cut quality and reducing costs.
Choosing the right plasma cutter from Vast means you’ll get a reliable tool that fits your budget and job needs right here in the U.S. Whether you’re fabricating at home or running a busy shop, there’s a Vast plasma cutter designed to help you work faster and cleaner.