Discover plasma cutting basics tips and tools for precise fast metal fabrication ideal for beginners DIY and small shops with vast equipment guidance.
If you’ve ever struggled to cut through metal cleanly and quickly, plasma cutting might just be the game-changer you’re looking for. This powerful, precise, and surprisingly affordable method lets you slice through steel, aluminum, and other conductive metals faster and cleaner than traditional tools. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast, small-shop owner, or hobby fabricator, mastering plasma cutting opens the door to professional-grade results without breaking the bank. In this guide, we’ll break down exactly how plasma cutting works, what gear you need, and insider tips to get you cutting like a pro—no experience required. Let’s jump in!
What is Plasma Cutting The Science Simplified
Plasma cutting is a powerful thermal cutting process that uses a high-temperature plasma arc to slice through metal quickly and precisely. Plasma itself is known as the fourth state of matter—beyond solid, liquid, and gas. It forms when gas is superheated to the point where electrons break free from atoms, creating an ionized, electrically conductive state. In plasma cutting, temperatures can soar between 20,000 and 30,000 degrees Fahrenheit, making it hot enough to melt metal almost instantly.
The process has roots dating back to the 1950s when it was first used for welding applications. Over time, plasma cutting evolved dramatically. Today’s CNC plasma tables bring precision and automation, allowing for intricate metal fabrication work that was once impossible with manual methods. This advancement puts plasma cutting in a league of its own for speed, accuracy, and versatility.
Key components make up every plasma cutting setup:
- Plasma torch: the handheld or mechanized tool that channels the plasma arc to the metal
- Power supply: converts electricity to create the plasma arc and controls cutting power
- Gas source: typically compressed air, nitrogen, or oxygen, which is ionized to form plasma
Together, these parts work seamlessly to make plasma cutting a staple for modern metal fabrication, mild steel cutting, and custom projects across farms, workshops, and factories alike.
How Does Plasma Cutting Work Step-by-Step Breakdown
Plasma cutting starts when a gas—usually air, nitrogen, or an inert gas—is blown through a narrow nozzle. Inside the plasma torch, this gas gets superheated by an electric arc, turning it into an ionized plasma. This plasma reaches temperatures up to 30,000°F, enough to melt through metal quickly.
Here’s the basic flow:
- Gas Ionization: The gas passes through the torch and is energized by an electric arc, becoming plasma.
- Molten Metal Ejection: The high-speed plasma jet cuts the metal by melting it and blowing away the molten metal from the cut.
To get the arc going, plasma cutters use different starting methods:
- High-Frequency Start: Uses a spark that jumps inside the torch to create the arc without touching the workpiece.
- Pilot Arc: Keeps a small, continuous arc inside the torch, allowing cutting over painted or rusty surfaces without interruption.
- Blowback Start: The simplest method, where the electrode touches the nozzle briefly to start the arc.
Gas choice depends on the metal and thickness you’re cutting:
- Air: Most common for mild steel; cost-effective and widely available.
- Nitrogen or Argon: Better for stainless steel and aluminum, offering cleaner cuts.
- Oxygen: Sometimes mixed for faster cutting on thicker steel.
Choosing the right gas improves cut quality and reduces dross, so match your gas to your material and thickness for the best results.
Plasma Cutting vs Other Methods When to Choose Plasma
When deciding on a cutting method, plasma cutting stands out for speed and versatility, especially on conductive metals like steel, aluminum, and copper. Here’s a quick look at how plasma cutting compares to oxy-fuel, laser, and waterjet cutting in speed and metal thickness handling:
| Cutting Method | Max Thickness (Mild Steel) | Cutting Speed (in/min) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasma Cutting | Up to 1.5 inches | 20-60 | Quick cuts on metal, medium thickness |
| Oxy-Fuel | Over 6 inches | 5-15 | Thick steel, slower precision cuts |
| Laser Cutting | Up to 0.5 inches | 30-100 | High precision, thin sheet metal |
| Waterjet | Over 6 inches | 10-30 | No heat damage, any material |
Pros of Plasma Cutting
- Fast and efficient on mild steel and other conductive metals
- Handles a broad thickness range (thin to moderately thick metal)
- Portable tools available, great for local shops and farm work
- Lower initial setup cost compared to lasers and waterjets
Cons of Plasma Cutting
- Not suited for non-conductive materials like plastics or glass
- Slightly rougher edge compared to laser or waterjet cuts
- Generates heat-affected zone and some dross
For local metal fabrication shops and farms, plasma cutting offers a perfect balance. Unlike the expensive laser machines, plasma cutters are easier to own, operate, and repair locally. Compared to oxy-fuel, plasma is much faster and cleaner on mild steel but doesn’t replace oxy-fuel for thick steel plate cutting.
For everyday projects—auto parts, farm repairs, or custom signs—a plasma cutter paired with a CNC plasma table provides precision without breaking the bank. It’s this blend of speed, cost-effectiveness, and adaptability that makes plasma cutting a go-to method in the U.S. metalworking scene.
Essential Equipment Building Your Plasma Cutting Setup with Vast
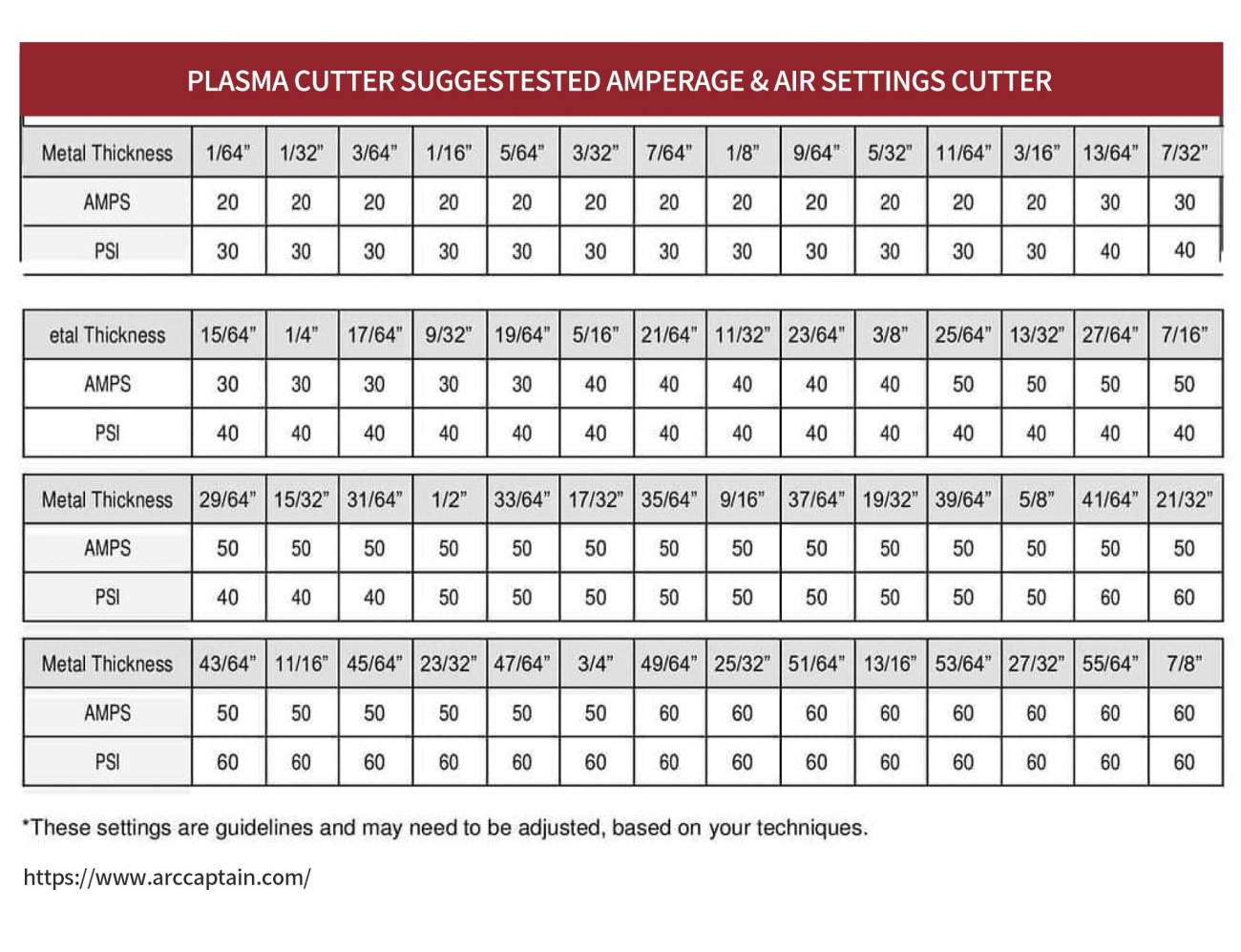
When setting up a plasma cutting workspace, having the right equipment makes all the difference. Here’s what you’ll need to get started with a reliable and efficient plasma cutter setup, especially if you plan to use Vast’s consumables and products.
Required Items for a Plasma Cutting Setup
- Power Supply: This is the heart of your plasma cutter. Make sure it provides steady power and matches your cutting needs, whether it’s for light DIY projects or heavier industrial work.
- Air Compressor: Clean, dry compressed air is essential for plasma cutting. Your compressor should deliver enough pressure and volume to keep the plasma arc stable.
- Plasma Torch and Consumables: The torch includes the nozzle, electrode, and shield—these wear out with use and need regular replacement. Vast’s consumables are known for durability and consistent cut quality, making them a smart choice.
- Gas Sources: Different types of plasma cutters may require specific gases (usually air, nitrogen, or argon mixes). Make sure you match the gas type according to your metal and thickness.
Types of Plasma Cutting Setups
- Handheld Plasma Cutters: These are great for on-the-go jobs like farm repairs or small local shop projects. They’re portable, easy to use, and ideal for cutting mild steel and other conductive metals.
- CNC Plasma Tables: For serious metal fabrication and precision cutting, CNC plasma tables offer automated, computer-controlled cutting. This setup boosts repeatability and accuracy, perfect for custom signs or industrial fabrication.
Budget Tips and Vast’s Consumables
- Investing in quality consumables from Vast can save money long-term by reducing downtime and improving cut quality.
- Consider starter kits for torch consumables, which offer a balance of price and variety.
- Don’t skimp on the air compressor—cheap units can introduce moisture and dirt that harm your torch.
- For local shops and farms, a handheld plasma cutter paired with Vast’s consumables offers a budget-friendly and dependable combo.
Setting up your plasma cutting station right with these essentials ensures smooth operation and professional results every time.
Safety First Protecting Yourself and Your Workspace

When working with plasma cutting, safety has to come first. The plasma arc gets insanely hot and can throw off molten metal sparks that cause serious burns or fires. UV light from the arc can damage your eyes and skin if you’re not protected. Here’s what you need to stay safe:
Safety Gear Checklist
- Protective lenses: Use a plasma cutting helmet or goggles with the right shade to block arc brightness and UV rays.
- Heavy gloves: Heat-resistant welding gloves protect your hands from sparks and hot metal.
- Jacket or sleeves: Wear flame-resistant clothing or a welding jacket to shield your arms and body.
- Ventilation: Good airflow or an exhaust system is critical to remove fumes and dust from your workspace.
Key Risks to Watch For
- Arc flash: Intense light from the plasma arc that can blind or burn your eyes without the proper eye protection.
- Molten splatter: Hot metal pieces that fly off during cutting — gloves and jackets can prevent burns.
- UV exposure: Prolonged exposure leads to skin burns and eye damage, so cover all exposed skin.
- Grounding: Properly ground your plasma cutter to cut electrical hazards and prevent shocks.
Workspace Preparation and OSHA Compliance
- Set up your plasma cutting area away from flammable materials and ensure a clean, dry floor.
- Keep a fire extinguisher within reach.
- Follow OSHA guidelines for electrical safety, ventilation requirements, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Make sure your setup complies with local and federal safety codes to protect yourself and others in the shop.
By keeping these safety tips front and center, you’ll protect your health and maintain a safe environment whether you’re working in a local shop, farm, or garage.
Step-by-Step How to Plasma Cut Like a Pro
Preparation Tips
- Clean your metal: Make sure your metal is free from rust, paint, oil, or dirt. This helps the plasma arc cut smoothly and improves cut quality.
- Set the right amperage: Check your plasma cutter’s manual and set the amps based on the metal thickness. Too low means slow cuts and rough edges; too high can burn through or waste consumables.
Cutting Technique
- Maintain torch standoff: Keep the plasma torch about 1/8 to 1/4 inch above the metal surface. Too close can cause damage to the consumables, too far leads to poor cut quality.
- Use steady speed: Move the torch at a consistent and even pace. Going too fast will leave uncut metal behind, too slow causes excessive dross and heat buildup.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Clamp the workpiece and ground the machine properly—a solid ground reduces arc issues.
- Secure the metal to your cutting surface so it doesn’t move.
- Select the correct gas and amperage based on the material type and thickness.
- Start the arc using your cutter’s method (high-frequency, pilot arc, or blowback).
- Hold the torch at the right standoff angle, usually perpendicular or slightly tilted forward.
- Begin cutting with a smooth, steady motion, following your marks or patterns.
- Finish the cut and slowly lift the torch away to avoid drag marks.
- Inspect and deburr the edges for a cleaner finish.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Ignoring air quality: Using unfiltered or moist air can clog your plasma cutter and ruin cuts.
- Wrong gas type: Using the incorrect plasma gas for your metal drastically lowers cut quality.
- Incorrect amperage settings: Too high or low amp settings harm cut consistency and consumable life.
- Poor grounding or clamping: This results in erratic arcs or wasted energy.
Following these tips will help you get clean cuts and extend your plasma cutting setup’s life, whether you’re working on farm repairs, local shop projects, or metal art.
Tips and Tricks Boosting Cut Quality for Local Projects
Getting clean, precise cuts with your plasma cutter doesn’t have to be tricky. When you’re working on custom signs or farm repairs around here, a few smart tweaks can make all the difference.
Troubleshooting Dross and Beveling Issues
- Dross buildup (that rough slag on the cut edge) often means your torch speed is off — try speeding up or slowing down to find that sweet spot.
- Check your air quality; moisture or oil in the gas causes poor cuts and excess dross. Make sure your compressor and filters are in good shape.
- For beveling problems, adjust your torch angle slightly — tilting it can help get clean, consistent bevels, especially for weld prep.
Local Hacks Using Vast Software
Many folks use vast software to sketch out their cutting plans. It’s great for designing custom metal farm signs, brackets, or small parts. This software helps you optimize cut paths, saving gas and reducing wear on consumables. Using software like this can speed up your projects and boost accuracy.
Advanced Uses
- Plasma cutting isn’t just for straight cuts. You can use it to gouge welds—removing bad weld beads or cleaning up edges.
- Beveling seams for welding prep is another handy trick when set up properly.
Maintenance Tips
- Replace plasma cutter consumables like nozzles and electrodes regularly. Worn parts cause poor cuts and more dross. Keep extras on hand to avoid downtime.
- Take care of your compressor by draining moisture daily and checking belts or filters. Clean, dry air is key to smooth plasma arcs and better cut quality.
Follow these simple tips and you’ll see a real upgrade in cut quality for your local projects, whether it’s for a small farm fix or a garage fabrication job.
Applications and Real-World Uses From Garage to Shop
Plasma cutting isn’t just for big factories—it’s perfect for local DIY projects and professional shops alike. In garages and home workshops, plasma cutters help create custom auto parts, metal art, and signage with clean cuts and minimal prep time. Whether you’re making brackets or intricate designs, the precise nature of plasma cutting adds professional-quality results even on a budget.
On the industrial side, plasma cutting is a go-to for metal fabrication, scrapping, and construction work. It handles everything from mild steel cutting to thicker industrial metals quickly and efficiently. Plasma cutters speed up the workflow by reducing the need for secondary finishing and deliver consistent cuts across various materials.
A great example is a local welder in the Midwest who upgraded to a CNC plasma table with Vast consumables. They saw a significant boost in cutting speed and edge quality, which translated into more jobs completed per week and less material waste. This kind of upgrade proves how plasma cutting, paired with reliable parts, makes a difference for local businesses competing with larger shops.
For anyone interested in metal fabrication or upgrading their cutting gear, plasma cutting offers a flexible, cost-effective tool that fits both garage enthusiasts and full-scale industrial users.
For more details on setting up a plasma cutting workstation, check out our guide on building your plasma cutting setup.