Explore vibrant aluminum anodizing colors with expert insights on processes, color options, durability, and applications for manufacturing and design.
If you’ve ever admired the stunning finishes on aluminum gadgets or architectural highlights, you’ve seen the magic of aluminum anodizing colors in action. But getting those vibrant, durable hues isn’t just about picking a shade—it’s a precise science that balances material, process, and pigment to deliver lasting impact. Whether you’re a designer, engineer, or DIY enthusiast, understanding how these colors come to life can transform your project from ordinary to eye-catching. Ready to unlock the secrets behind flawless anodized finishes and choose the perfect color for your next aluminum masterpiece? Let’s dive in!
The Science Behind Aluminum Anodizing
Aluminum anodizing is an electrochemical process that transforms the surface of aluminum into a durable, corrosion-resistant oxide layer. This oxide layer is what allows aluminum anodizing colors to adhere deeply and last much longer than ordinary paint or coating. At its core, the process involves immersing aluminum parts in an acid electrolyte bath while applying an electric current. Oxygen ions react with the aluminum surface, forming a porous aluminum oxide layer that’s hard, protective, and ready for coloring.
Core Process Breakdown
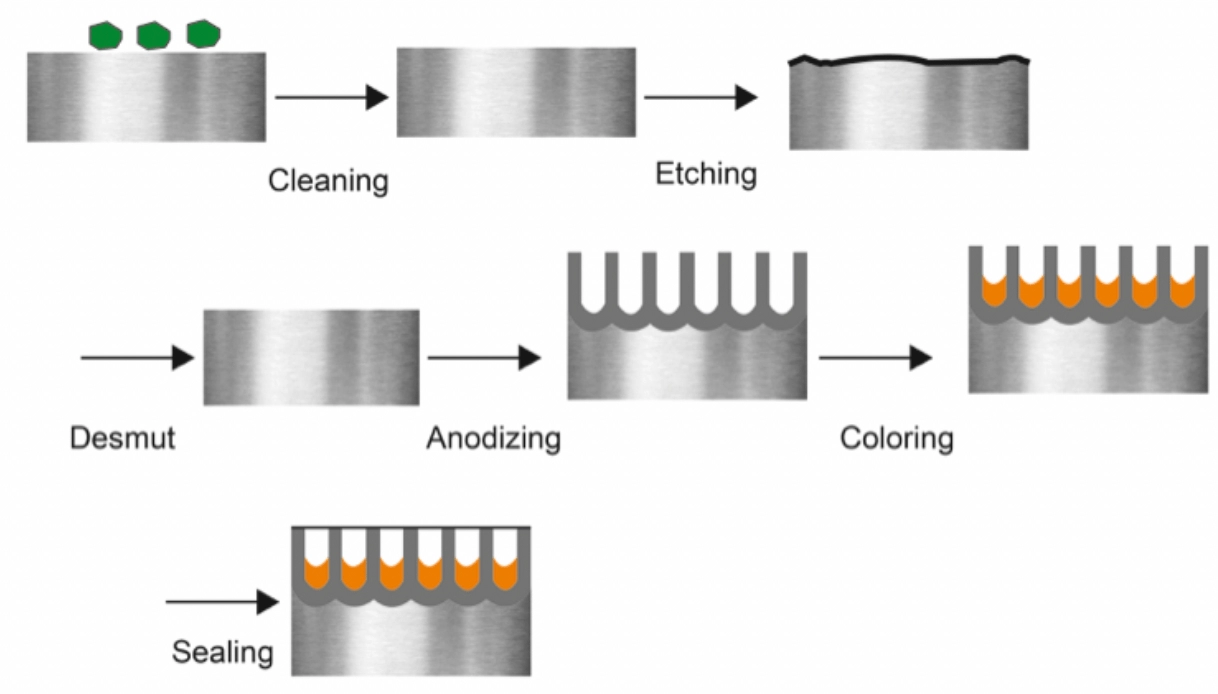
The anodizing process unfolds in a few basic steps:
- Cleaning: The aluminum is thoroughly cleaned to remove dirt, grease, and surface impurities.
- Etching and Brightening: This step enhances surface texture or shine, depending on the desired finish.
- Anodizing: The part is submerged in an acidic bath, where the electric current triggers formation of the oxide layer.
- Coloring: The porous oxide layer absorbs dyes or metallic salts to introduce color.
- Sealing: Finally, the oxide pores are sealed, locking in color and boosting corrosion resistance.
Types of Anodizing Relevant to Colors
There are different types of anodizing processes, but two are most common when it comes to coloring:
- Type II Anodizing (Sulfuric Acid Anodizing): This is the standard method for decorative colors. It produces a thinner oxide layer capable of absorbing a wide range of custom anodizing dyes.
- Type III Anodizing (Hardcoat or Hard Anodizing): This method results in a thicker, tougher coating that’s less porous. It’s great for wear resistance but offers limited color options, generally in natural or bronze anodizing shades.
Color Application Methods
Color gets embedded into the aluminum oxide layer primarily through two techniques:
- Organic Dyeing: Porous anodized surfaces soak up colored dyes. This gives a vibrant palette but may vary with alloy and process factors.
- Metallic Salts Coloring: Metal ions like nickel or cobalt infiltrate and react inside the pores, producing metallic or iridescent finishes. This method often yields richer, longer-lasting colors.
Key Insight
Understanding the science behind aluminum anodizing colors is crucial for picking the right combination of color, durability, and finish. The interplay between anodizing type, dye or metal salt use, and process control directly impacts your results. Whether you want bold architectural anodizing colors or subtly tinted industrial finishes, these basics guide informed choices for quality, lasting aluminum anodized finishes.
Exploring the Spectrum Popular and Custom Aluminum Anodizing Color Options
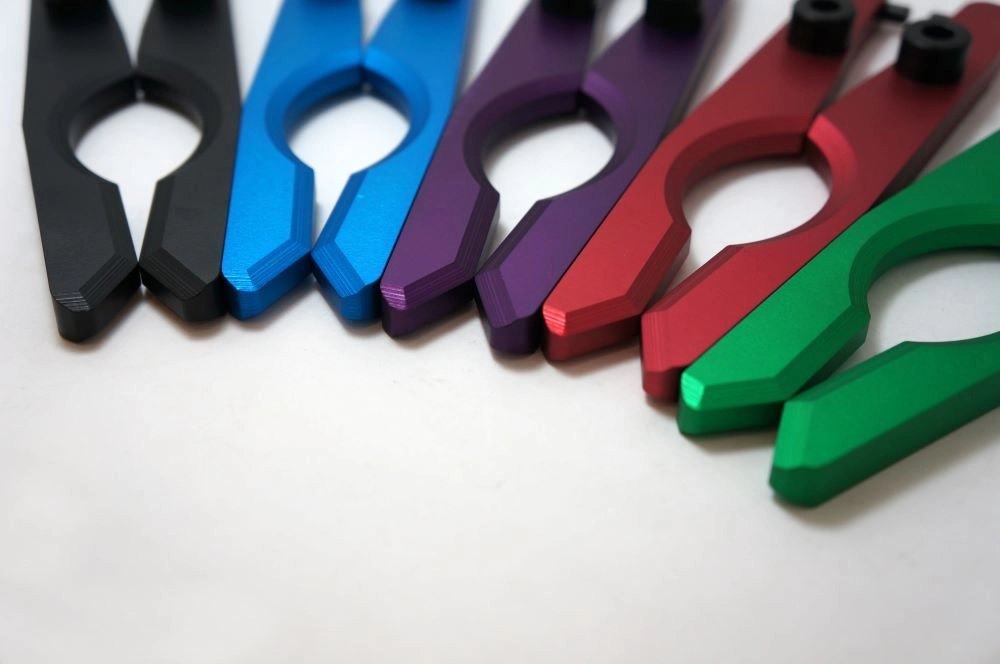

When it comes to aluminum anodizing colors, you’ll find a wide range of popular options that fit many industries and styles. The standard color palette usually includes classic shades like clear (natural finish), black, bronze, and champagne. These colors are popular because they offer durability and a consistent look, making them ideal for everything from architectural anodizing colors to consumer electronics.
But if you want to stand out, custom color capabilities open up a whole new world. Using custom anodizing dyes, manufacturers can produce rich blues, reds, greens, and even unique metallic effects. These colors are often tailored to match brand identities or specific design requirements. Keep in mind, the exact shade you get depends on factors like the aluminum alloy and the anodizing process used, so it’s important to work with a provider who understands those variances well.
Visual aids, such as color swatches or samples, are a great tool when selecting anodized aluminum finishes. They help you see how colors might look under different lighting conditions and let you compare standard colors versus custom options side by side. This hands-on approach can make a big difference in picking the right anodizing color for your project.
Factors Influencing Aluminum Anodizing Colors and Tips for Consistent Results

Getting the perfect aluminum anodizing colors can be tricky because several factors affect the final look. First, alloy and temper of the aluminum matter—a 6061 alloy will absorb dyes differently than a 5005, for example. The metal’s surface structure and hardness can change how vibrant or even the color appears.
Next, process variables play a big role. The anodizing type, like Type II (decorative) versus Type III (hardcoat anodizing process), changes the oxide layer thickness, affecting how dyes take and how the color holds up. Temperature, voltage, and timing during anodizing also tweak the results.
Environmental factors like humidity, air quality, and the water chemistry used in rinses can subtly shift colors and their durability. For example, UV exposure can fade some anodized colors unless you use UV-resistant anodized coatings.
To avoid problems and keep colors consistent:
- Use the same aluminum alloy and temper for each batch.
- Stick to precise process controls—temperature, time, and voltage.
- Employ custom anodizing dyes matched to your requirements.
- Test samples under expected environmental conditions.
- Store finished parts properly to prevent oxidation or damage.
If colors aren’t uniform, look at these troubleshooting tips:
- Check metal cleanliness—residual oils or dirt can cause blotches.
- Verify the electrolyte bath composition and freshness.
- Ensure the dye bath is filtered and properly heated.
- Review post-anodizing sealing methods; improper sealing can lead to color fading or corrosion.
Understanding these factors helps you get the rich, durable anodized aluminum finishes you want every time.
Applications and Industry Use Cases
Aluminum anodizing colors aren’t just about looks—they serve real purposes across many industries. Here’s where anodizing colors shine the most:
Architectural
In architecture, anodized aluminum provides durable, color-rich finishes used for window frames, curtain walls, and facades. Colors like bronze and champagne are popular for blending with building aesthetics while offering UV resistance and weather durability.
Consumer Electronics
Think smartphones, laptops, and tablets. Anodized aluminum finishes give gadgets sleek, scratch-resistant surfaces with a variety of colors that help brands stand out. Custom anodizing dyes create unique hues, making devices both stylish and durable.
Automotive and Aerospace
Anodizing colors offer corrosion resistance and tough finishes needed in automotive and aerospace parts. You’ll find anodized aluminum in trim, wheels, and interior components where hardcoat anodizing process ensures extra protection. Color options here can range from standard blacks and silvers to specialty bronze anodizing shades.
Medical and Industrial
Medical tools and industrial equipment benefit from anodized coatings that resist wear and tear while maintaining clean, sterilizable surfaces. Anodizing color variation factors help manufacturers pick shades that match safety and visibility standards.
Case Study
A Midwest-based electronics maker switched to custom anodizing colors for their laptop casings. They used UV-resistant anodized coatings to keep color vibrant under harsh lighting, reducing warranty returns by 15% due to surface damage.
In short, anodized aluminum finishes combine beauty and performance, making them essential across sectors that demand both.
Choosing the Right Anodizing Color
Picking the right aluminum anodizing colors can make a big difference in your project’s look and performance. Here are some practical tips to help you make the best choice without breaking the budget.
Practical Tips and Selection Framework
- Match the Color to the Use: Think about where the anodized aluminum will be used. For outdoor or architectural projects, UV-resistant anodized coatings in neutral or bronze anodizing shades work well. For consumer electronics or automotive parts, brighter custom anodizing dyes can add a modern touch.
- Consider Type II vs Type III Anodizing: Type II (standard anodizing) offers good color variety and surface finish. Type III (hardcoat anodizing process) is tougher and better for harsh environments, but color options can be more limited.
- Custom or Standard Colors: Choose from a standard color palette for quicker turnaround and lower cost. Custom colors allow more branding flexibility but usually come with a higher price tag.
Budget Breakdown
- Standard Colors: Usually cost-effective and suitable for most industrial anodizing applications.
- Custom Colors: May require extra setup time and specialized aluminum oxide coloring methods, increasing costs.
- Hardcoat Anodizing: Typically pricier due to thicker layers and specialized finishing processes, but it offers superior durability.
Maintenance and Longevity
- Anodized aluminum finishes are low maintenance but keep in mind:
- Regular cleaning with mild detergents preserves color.
- Avoid abrasive cleaning to prevent wear on the anodized layer.
- UV-resistant anodized coatings last longer outdoors, reducing fading.
Call to Action
Ready to add color and durability to your project? Reach out to a trusted anodizing supplier who understands the nuances of aluminum anodizing colors and can guide you through the process—whether you need standard bronze anodizing shades or a custom color match, there’s a solution for your needs.