Explore advanced automated assembly machines boosting precision efficiency and scalability in manufacturing with cutting-edge industrial automation solutions.
What is an Automated Assembly Machine
An automated assembly machine is specialized equipment designed to perform repetitive assembly tasks with minimal human intervention. Its core function is to streamline production by assembling components quickly, accurately, and consistently.
Core Functionality
- Automates repetitive tasks: Joins parts, inserts fasteners, or performs welding and testing.
- Maintains product consistency: Reduces errors found in manual assembly.
- Increases production speed: Operates continuously without fatigue.
Key Components and Operation Principles
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
| Actuators | Move parts and tools to assemble components |
| Sensors | Monitor positioning and quality control |
| Controllers | Coordinate machine tasks and timing |
| Feeding systems | Supply components automatically |
| Human-Machine Interface (HMI) | Allows operators to monitor and control processes |
These components work together using precise programming and control logic, ensuring each assembly step is executed correctly.
Automated vs Manual Assembly
Automated assembly machines outperform manual assembly in:
- Speed: Machines can operate 24/7 at a consistent pace.
- cURL Too many subrequests. Sensors and precise controls minimize errors.
- Labor costs: Reduces need for manual labor and training.
- Safety: Limits worker exposure to repetitive or hazardous tasks.
In contrast, manual assembly relies heavily on human dexterity and attention, making it less efficient, more prone to inconsistencies, and more costly for high-volume production.
Automated assembly machines transform industrial assembly automation by optimizing workflow and ensuring quality, forming the backbone of modern manufacturing processes.
Types of Automated Assembly Machines
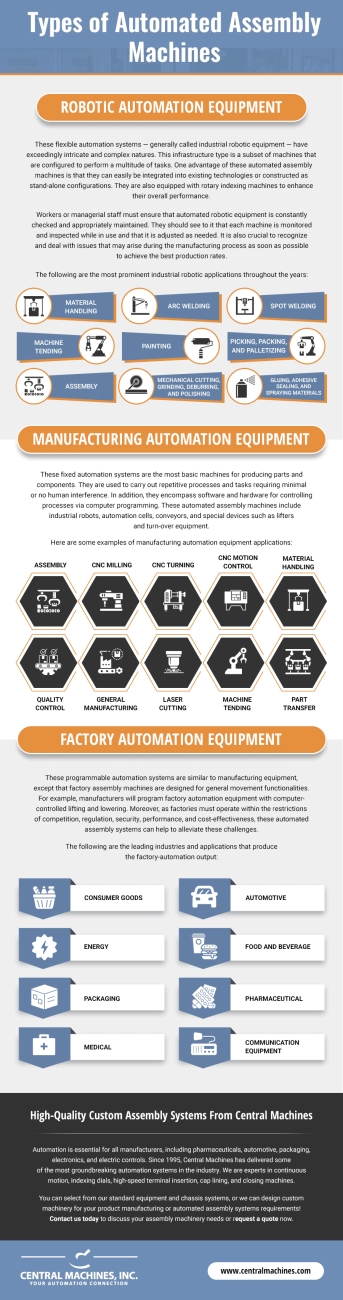
When looking at automated assembly machines, there are several common types used in U.S. industries, each designed to fit different production needs.
Pneumatic Assembly Machines
These use air pressure to control tools and parts. They’re great for fast, repetitive tasks like pressing or inserting components. Pneumatic systems are reliable and cost-effective for simple assembly jobs.
Robotic Assembly Systems
Robotic arms and automated cells fall into this category. These machines offer high precision and flexibility, handling complex tasks like welding, fastening, or electronic component placement. They’re essential for industries needing custom automation solutions.
Conveyor-Based Assembly Lines
These machines move parts along a fixed path, where different assembly operations happen at various stations. Conveyor systems boost production speed by streamlining workflow, perfect for mass production environments like automotive or consumer goods.
Hybrid Assembly Machines
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.

cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
| cURL Too many subrequests. | Impact |
|---|---|
| cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| cURL Too many subrequests. | cURL Too many subrequests. |
| cURL Too many subrequests. | Quick adjustments to production needs |
| Workplace Safety | Decreased injury risks and safer jobs |
Common Applications and Industries
Automated assembly machines are at the heart of many industries across the United States, helping to boost productivity and consistency. Here are the main sectors where these machines really shine:
- Electronics ManufacturingPrecise and efficient assembly is crucial in electronics. Automated assembly lines handle delicate components like circuit boards, connectors, and microchips faster than manual processes, ensuring fewer errors and higher quality.
- Automotive AssemblyIn auto manufacturing, robotic assembly machines are widely used for tasks such as fastening parts, welding, and installing components. Automation speeds up production while maintaining tight quality standards demanded by the industry.
- Consumer Goods ProductionFrom packaging household products to assembling small appliances, automated production machines enable fast, consistent output. This helps companies keep up with consumer demand and reduce labor costs.
- Medical Device AssemblyPrecision assembly systems are essential here since accuracy and cleanliness directly affect safety. Automated systems ensure consistent production of items like surgical instruments, diagnostic devices, and implants with minimal contamination risk.
- Aerospace and DefenseAssembly automation technology supports the production of complex aerospace parts with stringent quality and safety needs. It helps handle intricate assemblies efficiently while complying with regulatory standards.
These industries rely heavily on industrial assembly automation to improve quality, reduce errors, and speed up manufacturing—all crucial for staying competitive in the U.S. market. If you’re looking to optimize your production setup, choosing the right automated assembly machine tailored to your industry is key.
How to Choose the Right Automated Assembly Machine for Your Business
Choosing the right automated assembly machine is crucial for maximizing efficiency and return on investment. Here’s what to keep in mind:
Assess Production Volume and Complexity
- Volume: Know your daily or monthly output needs to pick a machine fast enough to keep up.
- Complexity: More intricate products may require advanced precision assembly systems or robotic assembly machines.
Evaluate Integration Compatibility
- Check if the new machine can easily connect with your current automated manufacturing equipment or existing assembly automation technology.
- Look for standard communication protocols and easy software compatibility.
Consider Flexibility and Future Scalability
- Choose a machine that can adapt to different product types or sizes.
- Make sure it supports upgrades or modular add-ons for future production changes.
Support and Maintenance Services
- Reliable service availability nearby is a must.
- Consider training programs for your operators.
- Look for straightforward maintenance with accessible troubleshooting guides.
Budget and ROI Considerations
| cURL Too many subrequests. | Details |
|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Assembly machine price and installation fees |
| Operating Costs | Energy usage, parts replacement, labor savings |
| ROI Timeline | How quickly efficiency gains offset costs |
| Long-term Value | Durability and upgradability |
By reviewing these points, you’ll find an automated assembly machine that fits your business needs and helps scale your production smartly.
Installation Training and Maintenance Best Practices
Getting your automated assembly machine up and running smoothly starts with a solid installation and setup. Here are a few key points for initial setup and calibration:
- Follow manufacturer guidelines carefully to ensure all components are installed correctly.
- Calibrate sensors and actuators based on your product specs to guarantee precision.
- cURL Too many subrequests. cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
- cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
cURL Too many subrequests.
Looking ahead, companies like VAST are driving next-generation assembly automation by emphasizing modular, adaptable systems. These machines are built for easy upgrades, letting manufacturers scale and customize their assembly lines as their needs evolve.
In short, automated assembly machines are becoming smarter, more user-friendly, and eco-conscious—ready to keep U.S. manufacturing competitive and efficient well into the future.