Explore how precise casting heat control enhances metal casting quality with expert tips on temperature management and heat treatment processes.
Analysis and Search Intent of Casting Heat
When people search for “casting heat,” they are often looking to understand how temperature impacts the metal casting process. They want to know how heat influences metal flow, solidification, and overall product quality. Others might be seeking practical advice on managing heat during casting to avoid defects like cracking or porosity. There is also a clear need for insights into different heating techniques, mold preheating, and post-casting heat treatments that ensure durability and precision.
In short, the main search intent revolves around:
- Understanding the role of heat in various casting methods
- Learning about temperature control and heat management techniques
- Identifying common heat-related casting problems and their solutions
- Exploring advances in heat technology for improved casting results
This knowledge is essential for manufacturers, metalworkers, and engineers who want to optimize their casting processes, improve product consistency, and reduce waste or rework caused by improper heat application.
Understanding Casting and the Role of Heat

Casting is a metalworking process where molten metal is poured into a mold to create a specific shape. Some common types include sand casting, die casting, and investment casting—each using different molds and methods depending on the final product’s needs.
Heat plays a crucial role in casting. First, the metal must be heated above its melting point so it can flow smoothly into the mold. This involves careful control of the metal casting temperature to ensure proper melting without overheating. Once poured, the metal cools and solidifies—this cooling stage affects the metal’s microstructure and overall strength.
Proper heat management during melting, pouring, and cooling ensures the metal flows well, fills every part of the mold, and avoids defects. If the heat isn’t right, issues like incomplete filling or weak spots in the part can happen. So, understanding the physics of heat transfer, including melting, solidification, and cooling rates, is essential for making strong, defect-free castings that meet quality standards.
Types of Heat in Casting

Heat plays several key roles throughout the casting process, starting with preheating molds. Preheating molds helps reduce thermal shock, improves metal flow, and prevents defects like cold shuts or incomplete filling. This step creates a stable environment so the molten metal cools more evenly.
Next is the heat of fusion—the energy needed to melt the metal. This thermal energy turns solid metal into liquid, allowing it to flow and fill the mold cavity. Proper control of this melting heat ensures smooth casting without overheating or underheating.
After casting, heat treatment phases like annealing, quenching, and tempering come into play. These processes use controlled heating and cooling to adjust the metal’s internal structure. Annealing softens the metal for easier machining, quenching hardens it quickly, and tempering balances hardness with toughness. Managing heat carefully in these phases directly affects the final product’s performance and durability.
Heat Management Techniques in Casting Processes
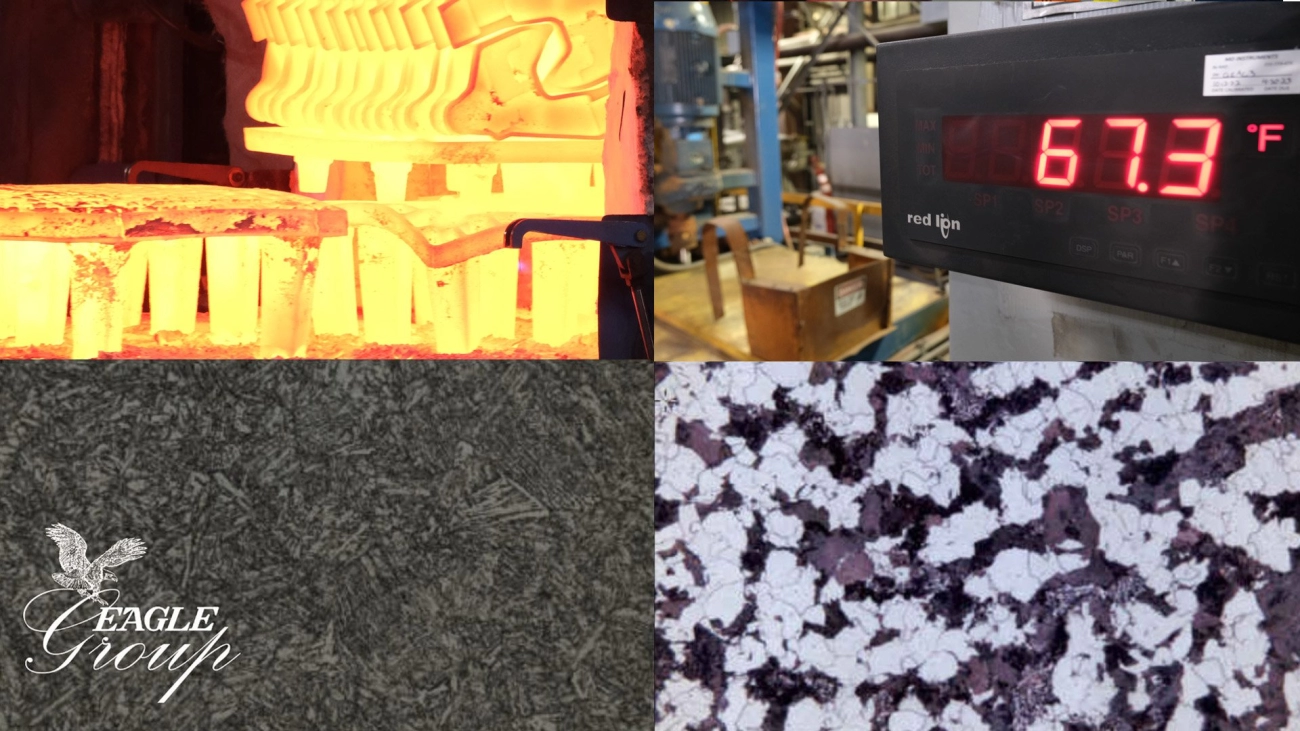
Managing heat properly is crucial for a successful casting process. Here’s how it works:
Controlled Heating Schedules and Temperature Profiles
- Following precise heating schedules ensures the metal reaches the right temperature without overheating or underheating.
- Gradual heating helps avoid thermal shock to molds and improves metal flow.
Types of Furnaces and Heating Equipment
- Induction furnaces offer fast, efficient heating with good temperature control.
- Electric arc furnaces handle high melting points and large batches.
- Gas-fired furnaces provide versatile heating options for various metals and molds.
Monitoring and Measurement Tools
- Thermocouples are common sensors used to track temperature inside furnaces and molds accurately.
- Infrared sensors measure surface temperatures without contact, useful for monitoring cooling.
Cooling Controls to Prevent Defects
- Proper cooling rate is essential to avoid shrinkage, cracking, and porosity.
- Controlled cooling avoids localized stresses and ensures even solidification.
- Using water sprays, air blasts, or cooling channels helps maintain consistent cooling speeds.
Together, these heat management techniques optimize metal casting temperature control and improve the overall quality of the final product.
Common Heat Related Challenges in Casting and How to Solve Them

Heat control is crucial in casting because too much or too little can cause defects. Some of the most common heat-related issues include:
- Shrinkage: Occurs when metal cools unevenly, causing parts to contract and leave gaps or weak spots.
- Porosity: Trapped gases or improper cooling can create tiny holes inside the metal, weakening the final product.
- Cracking: Rapid cooling or temperature changes can crack the metal, ruining its integrity.
Troubleshooting Overheating and Underheating
- Overheating can cause excess metal fluidity, leading to defects like metal erosion or distortion.
- Underheating leads to poor mold filling, resulting in cold shuts or incomplete castings.
Best Practices for Consistent Heat Application
- Use precise temperature controls and regular monitoring with thermocouples or infrared sensors.
- Maintain steady heating with carefully planned schedules to avoid rapid temperature swings.
- Preheat molds properly to reduce thermal shock and improve metal flow.
- Implement controlled cooling to manage the solidification process for better product quality.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
- Proper ventilation is essential to handle fumes and heat safely.
- Use insulated gloves, shields, and heat-resistant gear to protect workers.
- Regular equipment checks help avoid heat-related accidents.
- Managing energy use efficiently also reduces environmental impact.
By staying on top of these heat-related challenges, you can improve casting quality and maintain safety throughout the process.
Innovations and Trends in Casting Heat Technology
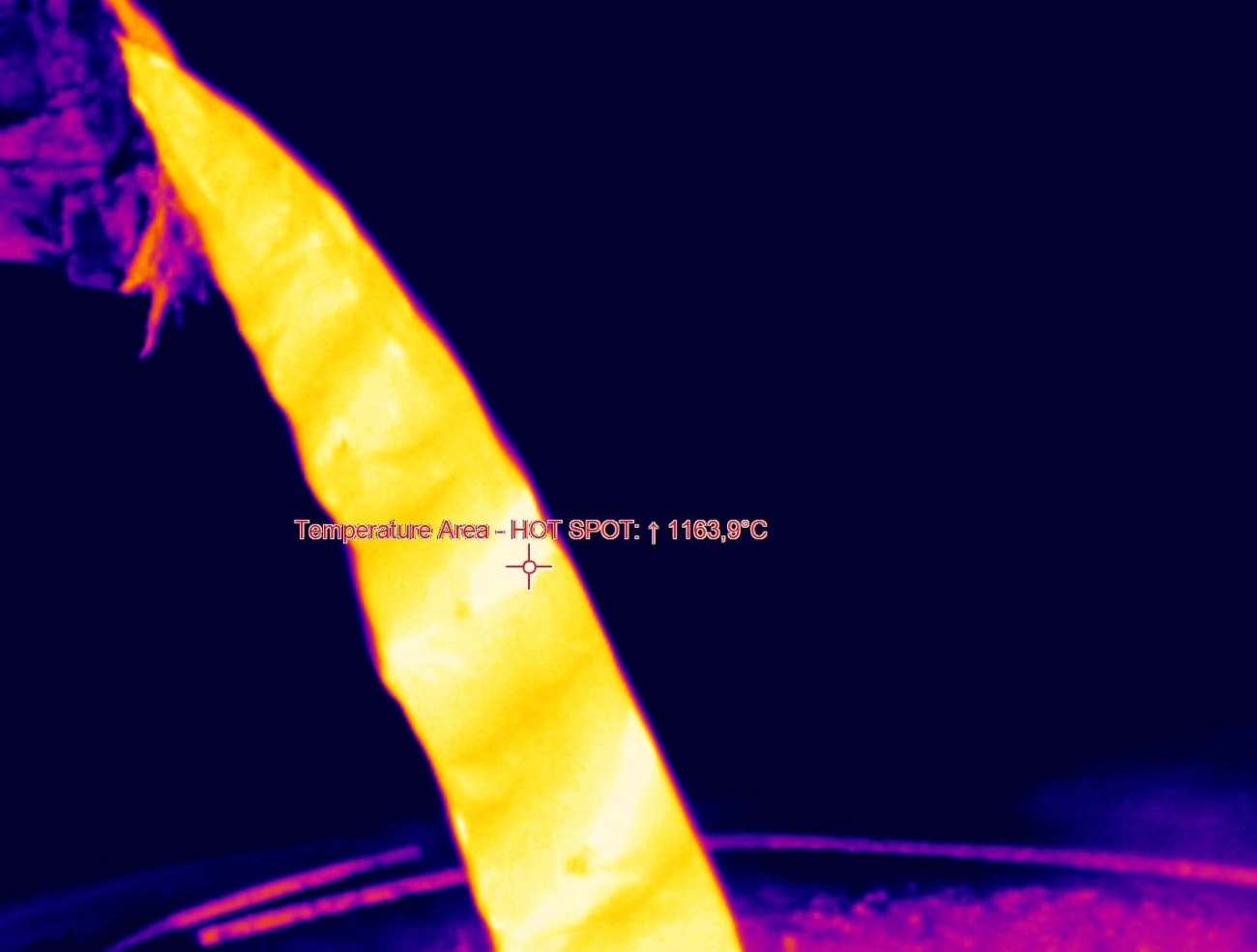

The casting industry is evolving fast when it comes to managing casting heat. Automation and the Internet of Things (IoT) have made temperature control smarter and more precise. Modern systems can monitor and adjust heat in real-time, helping to optimize the melting, mold preheating, and cooling phases without manual intervention.
Energy efficiency is another big trend. New heating methods focus on cutting fuel use and reducing waste heat, which saves money and lowers environmental impact. For example, induction furnaces and advanced gas-fired systems now offer better control and faster heating with less energy.
Sustainable practices are gaining traction, including recycling heat within the casting process and using greener materials. These innovations help meet stricter environmental regulations common in the U.S. market.
Some foundries have integrated smart sensors and thermal analysis software to catch temperature inconsistencies early, avoiding heat-related casting defects like porosity and shrinkage. These case studies highlight how better heat management boosts product quality and cuts production costs.
By adopting these innovations, foundries can stay competitive and produce higher-quality castings with improved energy savings and environmental responsibility.
How vast Supports Your Heat Casting Needs
At vast, we understand how crucial precise casting heat management is to producing high-quality metal parts. Our team brings deep expertise in metal casting temperature control and thermal analysis in casting, helping you optimize every stage from mold preheating to final cooling.
We offer advanced technologies designed for accurate heat control, including smart furnace systems and real-time monitoring tools like thermocouples and infrared sensors. These solutions help maintain consistent temperature profiles, reduce casting defects due to heat, and improve overall process efficiency.
Choosing vast means partnering with a team focused on innovation and reliability. We provide tailored services to meet your unique casting heat challenges, backed by responsive customer support. Our commitment is to help you achieve better product integrity while saving energy and cutting operational costs.